A thermocouple (0.8-mm-OD wire) used to measure the temperature of quiescent gas in a furnace gives a reading of 165°C. It is known, however, that the rate of radiant heat flow per meter length from the hotter furnace walls to the thermocouple wire is 1.1 W/m and the convective heat transfer coefficient between the wire and the gas is 6.8 W/(m2K). With this information, estimate the true gas temperature. State your assumptions and indicate the equations used.
GIVEN
• Thermocouple (0.8 mm OD wire) in a furnace
• Thermocouple reading (Tp) = 165°C
• Radiant heat transfer to the wire (qr/L) = 1.1 W/m
• Heat transfer coefficient ( ch ) = 6.8 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• Estimate the true gas temperature (TG)
ASSUMPTIONS
• The system is in equilibrium
• Conduction along the thermocouple is negligible
• Conduction between the thermocouple and the furnace wall is negligible
SKETCH
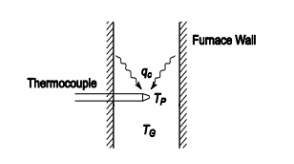
Equilibrium and the conservation of energy require that the heat gain of the probe by radiation if equal
to the heat lost by convection. The rate of heat transfer by convection is given
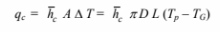
For steady state to exist the rate of heat transfer by convection must equal the rate of heat transfer by
radiation
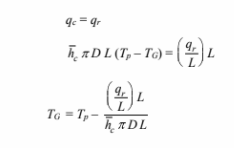
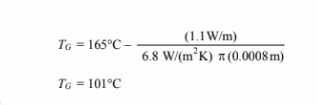
You might also like to view...
Which statement is true about Newton's First law of motion?
A. A body in motion has the tendency to come to a stop eventually. B. A body at rest stays at rest unless a force is applied to it. C. A body at rest stays at rest unless a force is applied to it and a body in motion stays in motion unless a force is applied to it. D. A body in motion stays in motion unless a force is applied to it. E. A body at rest stays at rest unless a force is applied to it and a body in motion has the tendency to come to a stop eventually.
________ in the early solar system might explain many of the observed irregularities
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
If the result of your calculations for a quantity has SI units of C2 ? s2/(kg ? m2), that quantity could be
A) an electric potential difference. B) a dielectric constant. C) an electric field strength. D) a capacitance. E) an electric potential energy.
The magnetic force on a charged particle moving at a constant speed in a uniform magnetic field will be doubled when the angle between the velocity of the particle and the direction of the magnetic field changes from 25.0° to
a. 57.7°. c. 12.2°. b. 12.5°. d. 50.0°.