If firms are competitive, then labor-market discrimination
a. cannot exist in either the short run or the long run.
b. will be more of a problem than if the market were monopolistic or imperfectly competitive.
c. likely will not be a long-run problem unless customers exhibit discriminatory preferences or government maintains discriminatory policies.
d. likely will be more of a problem in the long run than in the short run due to the zero-profit condition that characterizes long-run equilibrium for competitive firms.
c
You might also like to view...
A positive supply shock causes a leftward shift in the SRAS curve
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The strong interdependence of oligopolistic firms is shown by
A. their willingness to change prices frequently. B. their reluctance to advertise. C. their inability to form a price conspiracy. D. the vulnerability of their sales to the actions of their rivals.
In an open economy, the price of a bike is ________.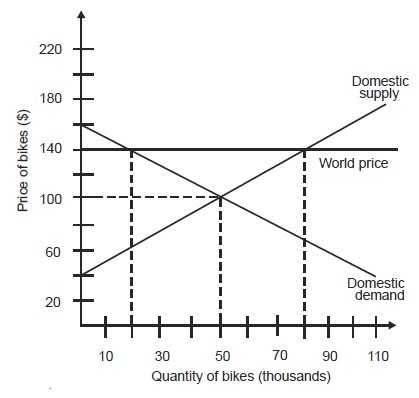
A. $100 B. $140 C. $40 D. $20
The free-rider problem can occur when
A. government deregulates the public transit system. B. welfare programs are not regulated well enough. C. public goods are provided to an individual who receives the benefit but does not pay for it. D. the government taxes a good or service.