Figure 5-16
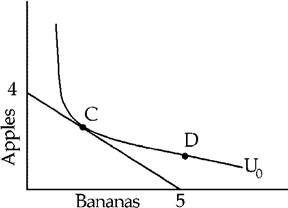
In Figure 5-16, Adam is
a.
better off at C than at D and able to afford either C or D.
b.
better off at D than at C but only able to afford C.
c.
equally well off at C and D and able to afford either C or D.
d.
equally well off at C and D but only able to afford C.
d
You might also like to view...
Assume that the market for consumer gasoline is perfectly competitive. When one additional seller (gas station) enters the market,
A) then at least one other seller must exit the market. B) the price of gasoline increases. C) the price of gasoline is left unaffected. D) the price of gasoline decreases. E) None of the above is correct.
With respect to each of the following issues, explain whether floating or fixed exchange-rates would be better and why it would be better.a. Internal monetary shocksb. External macroeconomic shocksc. A need for diversity in macroeconomic goals and policies across countries
What will be an ideal response?
The GDP deflator is equal to
A) real GDP divided by nominal GDP. B) nominal GDP divided by real GDP, multiplied by 100. C) nominal GDP divided by real GDP. D) real GDP divided by nominal GDP, multiplied by 100.
Goodwill can be a source of comparative advantage.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)