Explain how a pollution tax is different from a Pigouvian tax. Discuss how incentives for firms differ under the two types of taxes, and what would be required of the government if it were to structure a Pigouvian tax system to mimic the effects of a pollution tax.
What will be an ideal response?
A pollution tax imposes a tax on each unit of pollution that is emitted as a firm produces. A Pigouvian tax is a per-unit tax on the good that is being produced. In a particular market, a pollution tax can be set to result in the same decrease in output as an efficient Pigouvian tax -- but the pollution tax gives an incentive for firms to implement pollution abating technologies in production, whereas the Pigouvian tax gives no such incentive unless the government keeps re-setting the Pigouvian tax each time a firm implements pollution abating technologies.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is true?
A. Keynesians believe that consumers are inherently unstable in consumption decisions, but that businesses are relatively stable in making investment decisions. B. Monetarists believe in discretionary monetary policy. C. Lowering tax rates is the main priority of supply side economists. D. Supply-side economists believe in a heavily regulated economy.
Using the money demand and money supply model, show and explain why the Federal Reserve cannot achieve a target for both the money supply and an interest rate
What will be an ideal response?
To maximize profit, a natural monopolist produces the level of output at which
A. Marginal revenue equals marginal cost. B. Price equals average total cost. C. Price equals marginal cost. D. Marginal cost equals average total cost.
Refer to the diagram. At output level Q 2 :
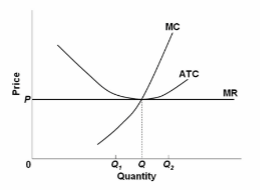
A. resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized.
B. resources are underallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized.
C. productive efficiency is achieved, but resources are underallocated to this product.
D. productive efficiency is achieved, but resources are overallocated to this product.