Define the following terms carefully:
(a) Full employment
(b) Purchasing power of money
(c) Real wage rate
(d) Relative price
What will be an ideal response?
(a) Full employment is a situation in which everyone who is willing and able to work can find a job. At full employment, the measured unemployment rate is still positive.(b) The purchasing power of a given sum of money is the volume of goods and services that it will buy.(c) The real wage rate is the wage rate adjusted for inflation. Specifically, it is the nominal wage divided by the price index. The real wage thus indicates the volume of goods and services that the nominal wages will buy.(d) An item’s relative price is its price in terms of some other item rather than in terms of dollars.
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.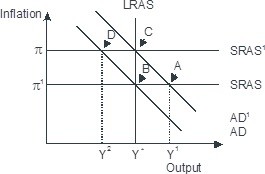
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary
How do markets for loans use signaling and screening to cope with private information?
What will be an ideal response?
The cost of trash removal goes up, in part at least, because labor productivity in auto manufacturing goes up
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Part-time workers who want full-time work are counted as
A. unemployed and therefore the official unemployment rate may overstate the level of unemployment. B. unemployed and therefore the official unemployment rate may understate the level of unemployment. C. fully employed and therefore the official unemployment rate may understate the level of unemployment. D. fully employed and therefore the official unemployment rate may overstate the level of unemployment.