Assuming a linear velocity distribution and a linear temperature distribution in the boundary layer over a flat plate, derive a relation between the thermal and hydrodynamic boundary-layer thicknesses and the Prandtl number.
GIVEN
Boundary layer over a flat plate
FIND
A relation between the thermal and hydrodynamic boundary-layer thicknesses and the Prandtl number
ASSUMPTIONS
Linear velocity and temperature distributions in the boundary layers
SKETCH
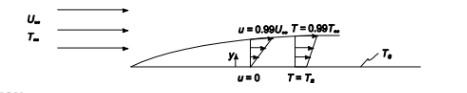
Let Absolute viscosity of the fluid = ?
Plate surface temperature = Ts
Bulk fluid temperature = T??
Bulk fluid viscosity = U??
Density of the fluid = p?
Thermal diffusivity of the fluid = a
The linear velocity profile will be used to solve the integral momentum equation first. The integral energy equation will then be solved and combined with the momentum solution.
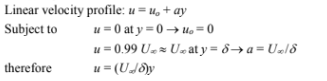
Substituting this into the integral momentum equation for a laminar boundary layer (Equation 5.42)
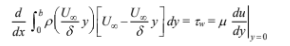
(The wall shear stress (Tw) is defined by Equation (4.2))
In this case, du/dy = constant = U?/?
Integrating
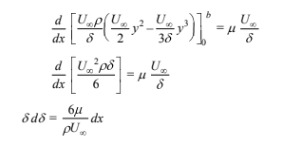
Integrating
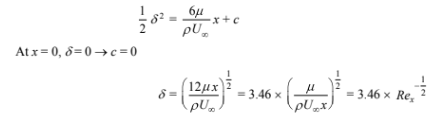
Linear temperature profile: T = To + by
Subject to T = Ts at y = 0 ? To = Ts
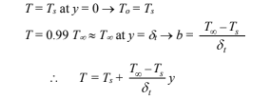
Substituting this and the expression for U into the integral energy equation of the laminar boundary layer for low speed flow (Equation 5.44)
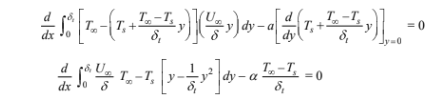
Integrating

Substituting Equation [1] into this expression
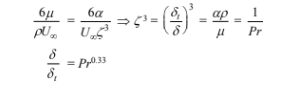
You might also like to view...
The idea that other civilizations are aware of our existence but have deliberately chosen to hide from us is referred to as the
A) zoo hypothesis B) conspiracy hypothesis C) sentinel hypothesis D) UFO hypothesis
What is the length of a simple pendulum with a period of 2.0 s?
A) 20 m B) 0.99 m C) 1.2 m D) 1.6 m E) 0.87 m
According to the nebular hypothesis, which of the following sequences of events are chronologically correct?
A. Solar nebula, interstellar cloud, collisions between planetesimals, accretion, planets B. interstellar cloud, Solar nebula, accretion, collisions between planetesimals, planets C. accretion, Solar nebula, interstellar cloud, collisions between planets, planetesimals D. interstellar cloud, accretion, Solar nebula, collisions between planetesimals, planets
The walls of cells are referred to by biologists as
A) linings B) coats C) shells D) membranes