A human-factors psychologist randomly assigns half of his participants to use Keyboard A and the other half to use Keyboard B. He measures the number of words per minute typed by people in each group. He suspects that Keyboard A is designed better and will therefore facilitate a higher words-per-minute rate. He conducts an independent-samples t-test and obtains the following results: What decision should he make regarding his hypothesis, and why?
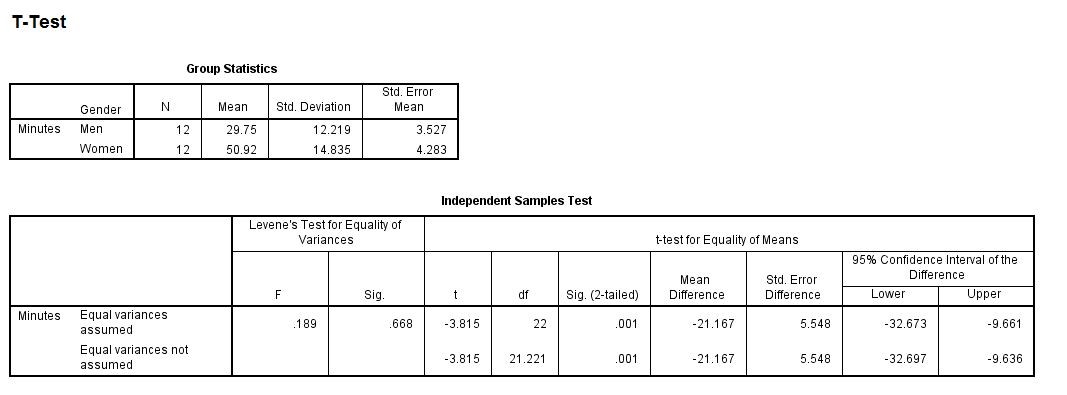
a. Reject the null hypothesis; typing speed is not affected by keyboard design.
b. Fail to reject the null hypothesis; typing speed is slower for Keyboard A than for Keyboard B.
c. Fail to reject the null hypothesis; typing speed is not affected by keyboard design.
d. Reject the null hypothesis; typing speed is faster for Keyboard A than for Keyboard B.
Ans: D
You might also like to view...
At approximately what age should a child first be able to successfully tie her or his shoes?
A. 8 to 9 years B. 4 to 5 years C. 6 to 7 years D. 10 to 11 years
Who tends to see their fate as out of their control?
a. externals c. auriculars b. internals d. arbitrators
Duncan is addicted to heroin and has to keep increasing his dosage to get the same effects. This effect of addiction is called
A. psychoactive dependence. B. psychological independence. C. drug tolerance. D. habituation.
Each of the following is linked to recovery from posttraumatic stress disorder EXCEPT ______
a. blocking out all painful memories associated with the traumatic event b. emotional support from family, friends, and the community c. immediate treatment near the site of the trauma d. an expectation that the individual will eventually return to everyday life