Describe what went wrong at Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and Fukushima
What will be an ideal response?
"While conducting a test of standby diesel generators, engineers disabled the power plant's safety system, withdrew the control rods, shut off the flow of steam to the generators, and decreased the flow of coolant water in the reactor. However, they did not allow for the radioactive heat energy generated by the fuel core, and the reactor began to heat up. The extra steam that was produced could not escape and had the effect of rapidly boosting the energy production of the reaction. In an attempt to quell the reactor, the engineers quickly inserted the carbon-tipped control rods. The carbon tips acted as moderators, slowing down the neutrons that were produced in the reaction. The neutrons, however, were still speedy enough to trigger more fission reactions, and the result was a split-second power surge to 100 times the maximum allowed level. Steam explosions then blew the 2,000-ton top off the reactor, the reactor melted down, and a fire was ignited in the graphite, burning for days."
"Three Mile Island nuclear power plant suffered a partial meltdown as a result of human and equipment failures and a flawed design. The steam generator shut down automatically because of a lack of power in its feed-water pumps, and eventually a valve on top of the generator opened in response to the gradual buildup of pressure. Unfortunately, the valve remained stuck in the open position and drained coolant water from the reactor vessel. There were no sensors to indicate that this pressure-operated relief valve was open. Operators responded poorly to the emergency, shutting down the emergency cooling system at one point and shutting down the pumps in the reactor vessel. One instrument error compounded the problem: Gauges told operators that the reactor was full of water when, actually, it needed water badly. The core was uncovered for a time and suffered a partial meltdown." The Rancho Seco nuclear power plant in Sacramento, California, had the same flawed design, which had not been corrected completely before the voters closed the facility in 1989, 10 years after the Three Mile Island accident.
At Fukushima, natural disasters were responsible. A major earthquake followed by a wall of water (tsunami) inundated the reactor and prevented the cooling of fuel rods, which led to explosions and the release of radioactive material into the surrounding area.
You might also like to view...
What is the elevation of this lowest location?
The question is based on this contour line map with elevations shown in feet.
• North is to the top of the map.
• Streams are shown with dashed lines.
• A graphic scale for measuring horizontal distances is shown below the map.
• Estimate elevations between contour lines to the nearest half-contour interval; assume that the top of a
hill is one-half-contour interval higher than the highest contour line shown.
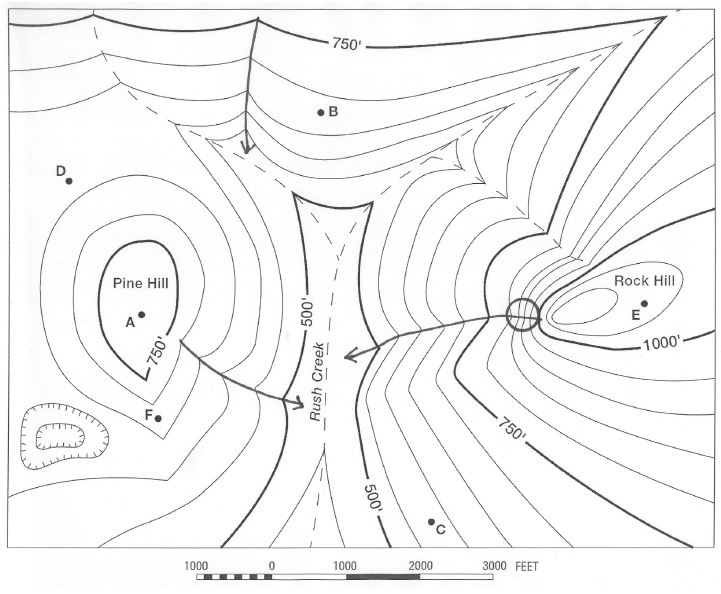
What will be an ideal response?
The greatest human impacts on ocean ecosystems are concentrated
A) in the northern hemisphere. B) around Australia. C) around South America. D) in the eastern Pacific.
The size of the Latin American region in land area is about
a. twice that of the United States. b. twice that of Europe. c. twice that of Australia. d. the same size as the United States.
Flowing air responding to the difference between higher and lower pressure is responding to the ________
A) pressure gradient B) Coriolis effect C) anticyclone D) intertropical convergence E) trade winds