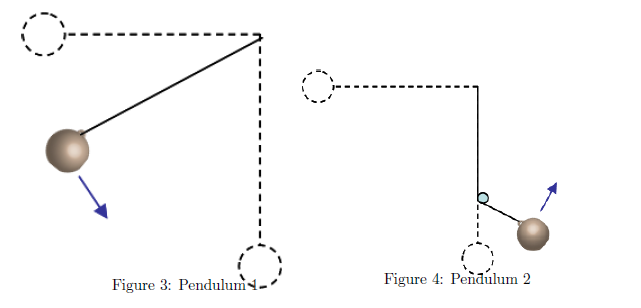
A mass m = 4.7 kg hangs on the end of a massless rope L = 2.05 m long. The pendulum is held horizontal and released from rest.
1) How fast is the mass moving at the bottom of its path?
2) What is the magnitude of the tension in the string at the bottom of the path?
3) If the maximum tension the string can take without breaking is Tmax = 382N, what is the maximum mass that can be used (Assuming that the mass is still released from the horizontal and swings down to its lowest point.)
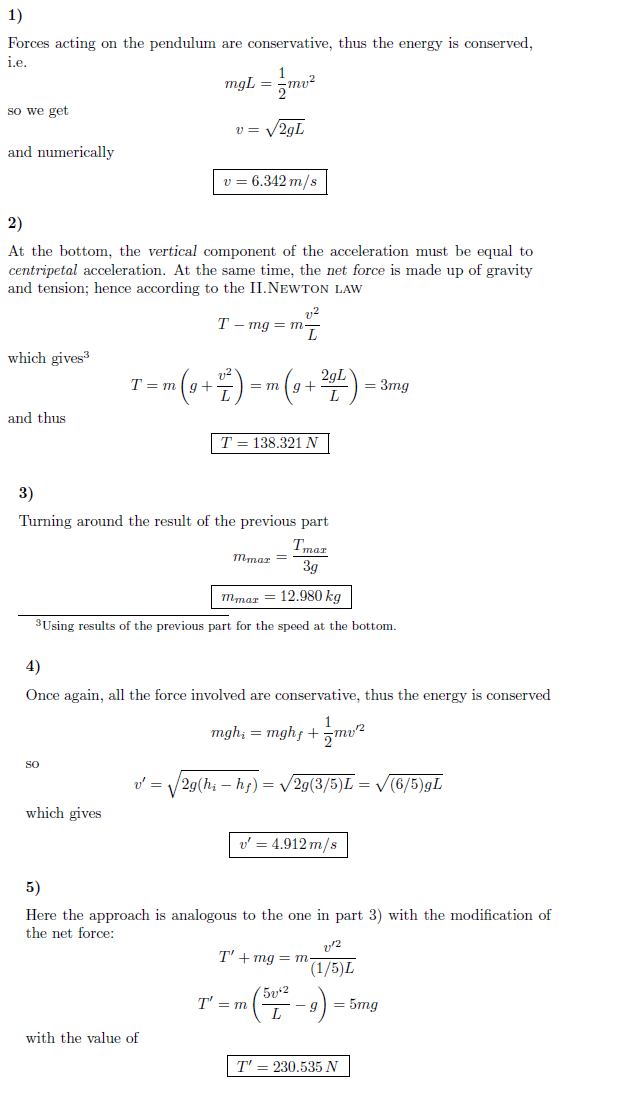
4) Now a peg is placed 4/5 of the way down the pendulum's path so that when the mass falls to its vertical position it hits and wraps around the peg. As it wraps around the peg and attains its maximum height it ends a distance of 3/5 L below its starting point (or 2/5 L from its lowest point). How fast is the mass moving at the top of its new path (directly above the peg)?
5) Using the original mass of m = 4.7 kg, what is the magnitude of the tension in the string at the top of the new path (directly above the peg)?
Answer:
You might also like to view...
Conversion of Units: An oak tree was planted 22 years ago. How many seconds does this correspond to? (Do not take leap days into account.)
A. 6.9 × 108 B. 1.2 × 107 C. 2.9 × 107 D. 2.8 × 108
How does the spectrum of a star depend on its surface temperature?
A. The cooler the star, the more molecular absorption bands will be present in its spectrum. B. Hot stars and cool stars can both have weak hydrogen lines. C. The hotter the star, the more colors will be present in its continuous spectrum. D. All of these choices are correct. E. None of these choices are correct.
When a current flows through an ionic liquid such as salty water, the moving charges are
A) only protons. B) only positive ions. C) only negative ions. D) only electrons. E) both positive and negative ions.
Fission and fusion reactions have in common _______
a. absorption of energy in the nuclear reaction b. high temperature requirements c. liberation of neutrons d. loss of mass of products over reactants e. gain in mass of products over reactants.