Labor productivity is calculated as
A) (real GDP ÷ aggregate hours).
B) (real GDP ÷ aggregate hours × number of workers).
C) (real GDP ÷ number of workers × ratio of capital per worker).
D) (real GDP ÷ technology level).
E) (real GDP ÷ aggregate hours × number of workers) × 100.
A
You might also like to view...
If the intended aim of the price floor set in the graph shown was a net increase in the well-being of producers, then positive analysis would have us consider:
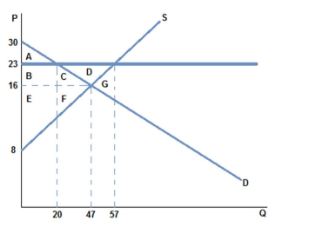
A. whether the surplus transferred from producers to consumers is larger than the consumer surplus lost to deadweight loss.
B. whether the surplus transferred from consumers to producers is larger than the consumer surplus lost to deadweight loss.
C. whether the producer surplus lost to deadweight loss is greater than the producer surplus gained from a higher price.
D. whether the producer surplus lost due to lower prices is greater than the producer surplus lost due to fewer transactions taking place.
"The money supply multiplied by velocity must equal GDP" is a statement of the
A) simple quantity theory of money. B) equation of exchange. C) modern quantity theory of money. D) all of the above
If government purchases increases by $1 million while net taxes are unchanged, then:
A. private saving increases. B. public saving does not change. C. public saving increases. D. public saving decreases.
When the price of a textbook is $100, 60 copies are demanded; and when the price of that textbook goes up to $120, 30 copies are demanded. In the price range between $100 and $120, the demand for the textbook is
A) elastic. B) inelastic. C) unit elastic. D) perfectly elastic.