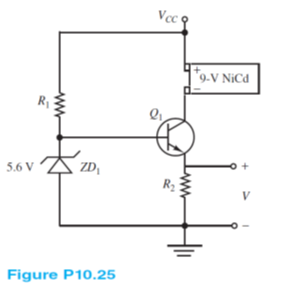
The circuit shown in Figure P10.25 is a 9-V battery charger. The purpose of the Zener diode is to provide a constant voltage across resistor R2, such that the transistor will source a constant emitter (and therefore collector) current. Select the values of R2, R1, and VCC such that the battery will be charged with a constant 40-mA current.
Known quantities:
The circuit of Figure P10.25: IC = 40 mA; Transistor large signal parameters.
Find:
Design a constant-current battery charging circuit, that is, find the values of VCC, R1, R2 that will cause the transistor Q1 to act as a 40-mA constant current source.
Assumptions:
Assume that the transistor is forward biased. Use the large-signal model with ? = 100.
Analysis:

You might also like to view...
What is the tradeoff for the work envelope of the Delta robot?
What will be an ideal response?
Which type of nail is commonly used for connections between framing members in wood light-frame structures? How do we specify the size of nails?
What will be an ideal response?
The term MOST-Likely used to describe anything that spins at driveshaft speed and vibrates only once every revolution is:
A. beat/boom vibration B. first order vibration C. second order vibration D. snapshot
A clunking noise during acceleration may be the result of a worn CV joint.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)