The age-associated changes that result in loss of accommodation of the eyes is called
A. myopia.
B. hyperopia.
C. presbyopia.
D. retinopia.
E. astigmatism.
C
You might also like to view...
The primary mechanism of water reabsorption in the kidney is
A. osmosis through aquaporins. B. bulk transport by means of endocytosis. C. secondary active transport by means of a sodium-water symporter. D. primary active transport by means of a protein pump.
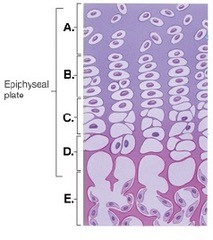 This figure illustrates bone growth in length at the epiphyseal plate. Zone "E" represents
This figure illustrates bone growth in length at the epiphyseal plate. Zone "E" represents
A. zone of hypertrophy. B. zone of calcification. C. bone tissue of the diaphysis. D. zone of resting cartilage. E. zone of proliferation.
A neuroglial cell ________
A) supports neurons B) conducts electrical impulses along axons C) receives electrical impulses from sensory organs D) conducts electrical impulses between neurons
The most inferior part of the sternum is called the
A. manubrium. B. costal cartilage. C. clavicle. D. xiphoid process.