A leftward shift of the demand curve results in:
a. increase in equilibrium price
b. increase in quantity.
c. decrease in both equilibrium price and quantity.
d. decrease in quantity and an indeterminate equilibrium price.
c
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as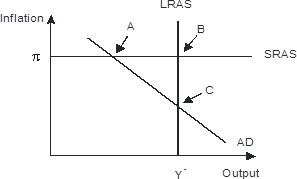
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
In the equation of exchange, the letter "V" stands for
A) variance. B) validity. C) volume. D) velocity.
Suppose that a union successfully negotiated a 10 percent wage increase and the quantity of labor demanded increased by 10 percent. We can conclude that:
A. the labor demand curve must have independently shifted to the right. B. labor demand is highly elastic. C. the coefficient of labor demand elasticity is less than 1. D. labor demand is unit-elastic.
Positive economics
A. always gives an optimistic spin to economic news. B. was not used by nineteenth century economists. C. is concerned with the economic policies that should be implemented. D. is objective.