The relationship between the marginal product of labor (MP), the product price (P) and the marginal revenue product of labor (MRP) in a perfectly competitive market is
a. MP = P x MRP
b. MP = P + MRP
c. MRP = P / MP
d. MRP = P x MP
e. MRP = P + MP
D
You might also like to view...
Refer to Excise Subsidy. The deadweight loss created by the subsidy is represented by
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram which shows the effects of an excise subsidy given to firms. The initial price and quantity are P0 and Q0, respectively. After the subsidy is granted, the equilibrium quantity is Q1, firms receive the price Ps, and consumers pay the price Pd.
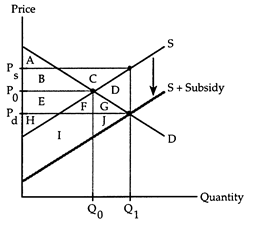
a. area F + G.
b. area D + G + J.
c. area C.
d. area D.
The United Auto Workers is striking against Ford. The Teamsters refuse to deliver steel to Ford. This is an example of
A) a jurisdictional dispute and is illegal under the Taft-Hartley Act. B) a secondary boycott and is illegal under the Taft-Hartley Act. C) a sympathy strike and is illegal under the Taft-Hartley Act. D) a closed shop and is illegal under the Wagner Act.
The proponents of fixed exchange rates argue that flexible exchange rates
A) hamper international trade because of uncertainty over what the exchange rate will be. B) force a nation to use its domestic macroeconomic policies to maintain an exchange rate. C) lead to trade protectionism. D) a and b E) a, b, and c
Over the past 30 years, most countries have moved toward
A. closing the economy to imports. B. more government regulation of the economy. C. less government regulation of the economy. D. planned central economies.