The expected damage to innocent third parties per unit of the good produced is shown as the "external cost" in Figure 27.1. An unregulated competitive market for the product produces a quantity of Q* units, which sell for a price of P* per unit. The competitive industry would produce the socially optimal quantity of this product if the expected per unit cost to producers of this product due to just and reasonable lawsuits were 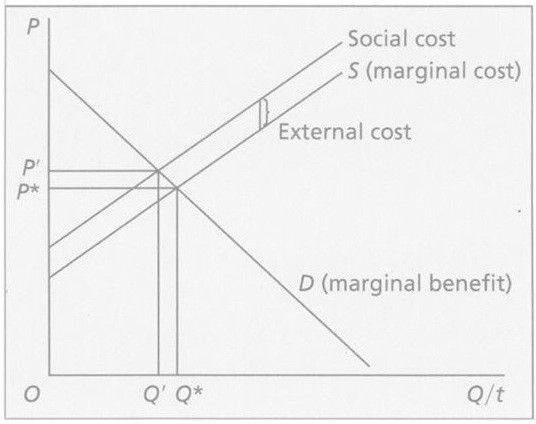
A. greater than the external cost.
B. equal to the external cost.
C. greater than zero but less than the external cost.
D. zero.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Other things equal, a decrease in autonomous consumption shifts the ________ curve to the ________
A) IS; right B) IS; left C) LM; left D) LM; right
Since a firm is willing to sell its product at the marginal cost and since the firm receives the market price, the difference between the two is:
a. consumer surplus. b. economic profit. c. marginal revenue. d. producer surplus. e. a shortage.
If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.75 and the equilibrium national income level is $500 billion, then a $25 billion increase in aggregate expenditure will cause the aggregate expenditure curve to shift
a. downward and national income to decrease by $33.3 billion b. upward and national income to increase by $33.3 billion c. downward and national income to increase by $25 billion d. upward and national income to increase by $100 billion e. upward and national income to decrease by $100 billion
If two goods are substitutes, then
A. there is an inverse relationship between changes in the price of one good and changes in the demand for the other. B. changes in the quantity demanded of one good will not affect the demand for the other. C. an increase in the price of one causes the demand for the other to fall. D. if the price of one good falls, the demand for the other good falls also.