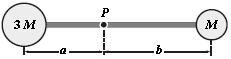
The rigid body shown is rotated about an axis perpendicular to the paper and through the point P. If M = 0.40 kg, a = 30 cm, and b = 50 cm, how much work is required to take the body from rest to an angular speed of 5.0 rad/s? Neglect the mass of the connecting rods and treat the masses as particles
a.
2.9 J
b.
2.6 J
c.
3.1 J
d.
3.4 J
e.
1.6 J
b
You might also like to view...
Friction: The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between a 3.0-kg box and a horizontal desktop are 0.40 and 0.30, respectively. What is the force of friction on the box when a 15-N horizontal push is applied to the box?
A. 12 N B. 8.8 N C. 15 N D. 6.0 N E. 4.5 N
The diameter of the sun is 1.39*109 m. Estimate the percentage of the total radiation emitted by the sun, which approximates a blackbody at 5760 K, that is actually intercepted by the Earth. Of the total radiation falling on the Earth, about 70% falls on the ocean. Estimate the amount of radiation from the sun that falls on land, and then estimate the ratio of energy currently used worldwide and the amount of terrestrial solar energy that is available. Discuss why all of the energy cannot be harnessed.
GIVEN • Diameter of sun (Ds)= 1.39*109 m • Sun is approximate black body at temperature (Ts) =5760 K • 70% of radiation falls on the ocean. • Diameter of the earth (De)= 1.27*107 m • Distance between sun and earth (Rse )=1.53*1011 m FIND • Amount of radiation from sun that falls on land • Ratio of energy currently used worldwide and the amount of terrestrial solar energy that is available. • Discuss why all energy cannot be harnessed. ASSUMPTIONS • The sun’s radiation is assumed as ideal black body radiation.
The greatest contribution of the Greeks to modern thought was:
A) the idea that all the planets orbited the Sun. B) that their mythology was the basis for the naming of the constellations. C) that their observation of stellar parallax proved the Earth orbited the Sun. D) the development of scientific inquiry and model building. E) the invention of the telescope.
A beam of X-rays of different frequencies is reflected at 10 degrees off a crystal of interatomic spacing 0.2 nm. Which X-ray wavelength is preferentially reflected?
a. 0.0943 nm b. 0.139 nm c. 0.0695 nm d. 1.02 × 10^?10 m e. 3.47 × 10^?11 m