Initially, a pharmacy with a volume of 35,000 had fixed costs of $200,000 and variable costs of $140,000. After remodeling, its fixed costs fell to $100,000, even though its volume and variable costs were unchanged. As a result,
A. its infra-marginal costs will be lower.
B. its incremental costs will be lower.
C. its average costs will be lower.
D. All of the above
C. its average costs will be lower.
You might also like to view...
When a positive externality is present in a market, the quantity consumed:
A. is always more than the socially optimal quantity. B. is the same as the socially optimal quantity. C. is often more than the socially optimal quantity. D. is less than the socially optimal quantity.
In a country with a working-age population of 200 million, 140 million people are employed and 20 million are unemployed. The size of the labor force is
What will be an ideal response?
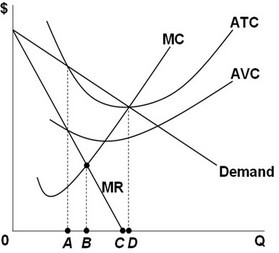 On the graph above, what is the profit-maximizing level of output for a pure monopolist?
On the graph above, what is the profit-maximizing level of output for a pure monopolist?
A. A B. B C. C D. D
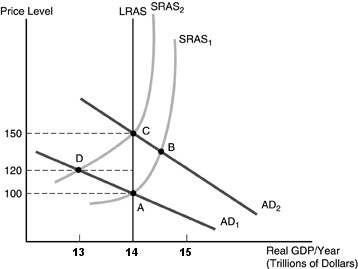 Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A, and the government initiates an expansionary monetary policy to increase aggregate demand. Which of the following is a TRUE statement concerning the differences between what happens when the central bank action is unanticipated and when it is anticipated?
Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A, and the government initiates an expansionary monetary policy to increase aggregate demand. Which of the following is a TRUE statement concerning the differences between what happens when the central bank action is unanticipated and when it is anticipated?
A. The new long-run equilibrium is point C in either case. When the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated, the new short-run equilibrium is point B, but when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated the new short-run equilibrium is point D. B. The new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated is point B while the new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated is point A. C. The new long-run equilibrium will be point C in either case. When the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated, the economy moves to B in the short run, but when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated, short-run aggregate supply shifts when the aggregate demand curve shifts, and the economy moves immediately to point C. D. The new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated is point B while the new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated is point C.