Refer to the given market-for-money diagrams. If the interest rate was at 8 percent, people would:
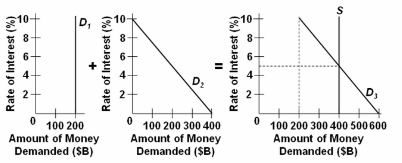
A. sell bonds, which would cause bond prices to fall and the interest rate to fall.
B. buy bonds, which would cause bond prices to rise and the interest rate to fall.
C. have insufficient liquidity, which would cause them to reduce their spending on consumer
goods.
D. buy bonds, which would cause bond prices to fall and the interest rate to rise.
B. buy bonds, which would cause bond prices to rise and the interest rate to fall
You might also like to view...
Holding large amounts of bank capital helps prevent bank failures because
A) it means that the bank has a higher income. B) it makes loans easier to sell. C) it can be used to absorb the losses resulting from bad loans. D) it makes it easier to call in loans.
Suppose a technological innovation shifts the marginal cost curve downward. Which one of the following cost curves does NOT shift?
A) Firm's short-run supply curve B) Average total cost curve C) Average variable cost curve D) Average fixed cost curve
The "no shirking constraint" (NSC) curve never crosses the supply of labor curve, so
A) the market never reaches equilibrium. B) there is always full employment in equilibrium. C) there is always some unemployment in equilibrium. D) the efficiency wage is always lower than the market-clearing wage. E) the gap between the NSC curve and the supply of labor curve equals the difference between the efficiency wage and the market-clearing wage.
Deadweight loss is the
a. decline in total surplus that results from a tax. b. decline in government revenue when taxes are reduced in a market. c. decline in consumer surplus when a tax is placed on buyers. d. loss of profits to business firms when a tax is imposed.