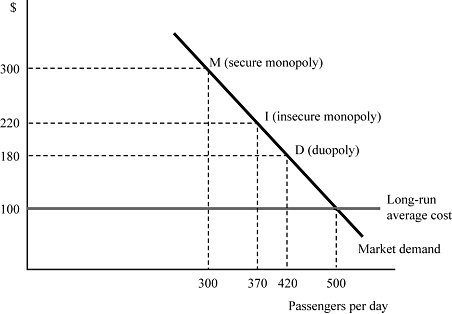
 In Figure 8.10, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit-maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is zero passengers per day, what is Fly Smart's profit when it commits to the entry-deterring quantity?
In Figure 8.10, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit-maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is zero passengers per day, what is Fly Smart's profit when it commits to the entry-deterring quantity?
A. $60,000
B. $44,400
C. $33,600
D. $0
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Where pollution is prevalent, we might expect that
a. externalities are being effectively internalized b. marginal social costs are greater than marginal private costs c. marginal costs are greater than marginal benefits d. marginal private costs are greater than marginal social costs e. externalities are not important
An assumption behind the infant industry argument for tariff protection is that
A) foreign competitors are selling output below average cost. B) the domestic industry will be facing an upward adjustment in its average cost. C) the domestic industry will eventually gain comparative advantage in producing the good. D) the market needs additional competition to satisfy consumer demand.
Marginal profit is the profit
a. earned by a firm that is about to go out of business. b. calculated directly from the total cost curve. c. that is added by a one-unit increase in total output. d. earned for each dollar of cost increase.
Figure 7-13
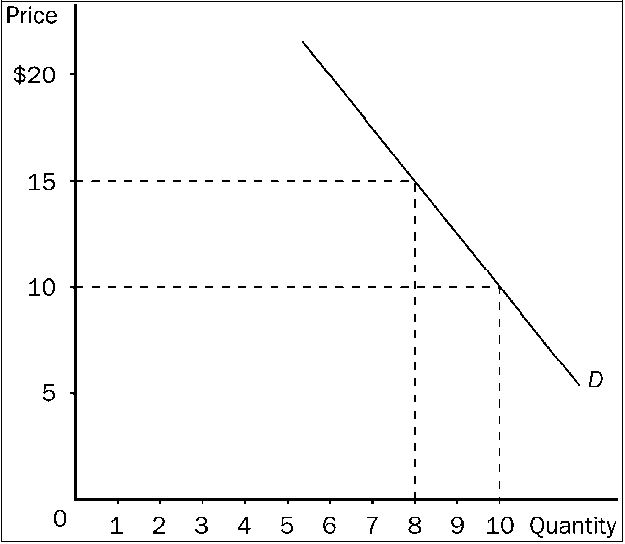
Refer to . A decrease in price from $15 to $10 leads to
a.
a decrease in total revenue of $10, so the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1 in this price range.
b.
a decrease in total revenue of $10, so the price elasticity of demand is less than 1 in this price range.
c.
a decrease in total revenue of $20, so the price elasticity of demand is less than 1 in this price range.
d.
a decrease in total revenue of $20, so demand is elastic in this price range.