Compared to a pollution? tax, a? uniform-abatement policy is less efficient because it does not exploit differences in??
Compared to a pollution? tax, a? uniform-abatement policy is
less
efficient because it does not exploit differences in??
A.
output levels across firms.
B.
the level of environmental concern across firms.
C.
abatement costs across firms.
Your answer is correct.
D.
all of the above.
less
C. - abatement costs across firms.
You might also like to view...
In the mid-1970s, antitrust policy began a new phase characterized by
a. the use of per se rules. b. reliance on economic analysis. c. the definition of a monopoly as a firm with dominant market share. d. repeal of the Clayton Act.
Some economists argue that there is no such thing as a short-run Phillips curve. Who are these economists and what is their argument?
Figure 4-3
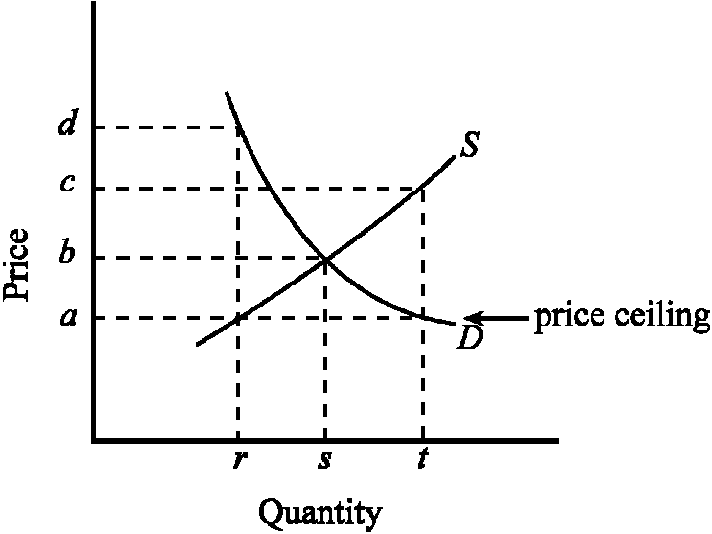
indicates the demand (D) and supply (S) for the rental housing market in a large city. If the government imposed a price ceiling of a, which of the following would be true?
a.
The quantity of rental housing demanded would be t.
b.
The quantity of rental housing supplied would be r.
c.
There would be a shortage of rental housing.
d.
All of the above are true.
The IMF offers loans to developing countries in times of balance of payment constraints, but the IMF also faces strong criticisms because:
A. contractionary fiscal policy and expansionary monetary policy tend to be ineffective against balance of payment constraints. B. contractionary fiscal and monetary policies are always undesirable for any developing country. C. it employs economists that know little about developing countries and their economic affairs. D. the conditions tend to be procyclical, therefore worsening the recessions.