Consider a monopolist facing a linear (inverse) demand curve given by:
p = a - bQ
Show with calculus that the marginal revenue in fact has the same price-axis intercept but twice the slope as the inverse demand curve above.
Total Revenue = (a - bQ)Q. MR = dTR/dQ = a - 2bQ.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the table below. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is Big Oaks' marginal cost of producing between points B and C on their production possibilities frontier?
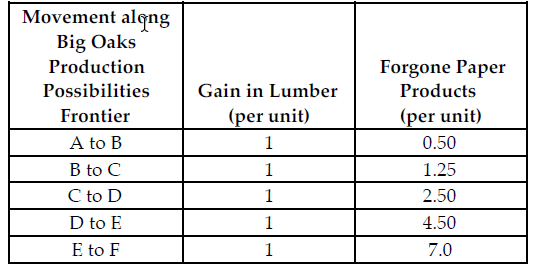
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) $1.25
B) $6.25
C) $5.50
D) $2.50
If in the long run, imports are paid for by exports, then
A) any restriction of imports ultimately reduces exports. B) any restriction of imports ultimately expands exports. C) any restriction of imports has no impact on exports. D) any restriction of exports has no impact on imports.
The importance of the ceteris paribus assumption is that it: a. allows one to separate normative economic issues from positive economic ones
b. allows one to generalize from the whole to the individual. c. allows one to analyze the relationship between two variables apart from the influence of other variables. d. allows one to hold all variables constant so the economy can be carefully observed in a suspended state.
Nonactivists argue against the use of discretionary monetary policy and rules-based monetary policy
Indicate whether the statement is true or false