The total cost to a firm of producing zero units of output is
a. zero in both the short run and the long run
b. its fixed cost in the short run, zero in the long run
c. its fixed cost in the long run, zero in the short run
d. its fixed cost in both the short run and the long run
e. its variable cost in both the short run and the long run
B
You might also like to view...
Ocean Spray is considered to be an oligopoly firm because, until the 1990s, it faced little competition in the market for fresh and frozen cranberries. Why?
A) Ocean Spray had a patent on the production of cranberries that gave the company the exclusive right to market its product for 20 years. The 20-year period ended in the 1990s. B) The federal government imposed a high tariff on cranberry imports. During the 1990s the tariff was eliminated, but Ocean Spray still controls about 80 percent of the cranberry market. C) Until the 1990s, Ocean Spray controlled almost the entire supply of cranberries. D) Ocean Spray was able to achieve significant economies of scale in the production of cranberries. Beginning in the 1990s, other firms finally achieved economies of scale as well, but Ocean Spray still controls about 80 percent of the cranberry market.
Imagine that a country is at point X of this production possibilities frontier and a country is at point Y.
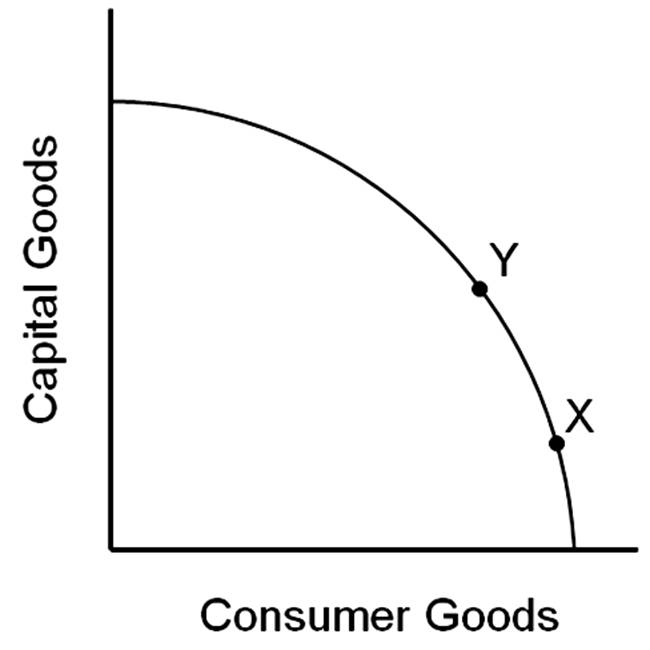
A. The country at point X will probably grow faster than the country at point Y.
B. The country at point Y will probably grow faster than the country at point X.
C. The two countries will probably grow at about the same speed.
D. There is no way of predicting which country will grow faster.
At any quantity, the marginal factor cost for a monopsonist is always
A. above the labor supply curve. B. parallel to the marginal revenue product. C. below the labor supply curve. D. above the labor demand curve.
The problem of having unlimited wants under the constraint of limited resources can describe the problem of:
A. scarcity. B. the marginal principle. C. sunk costs. D. opportunity cost.