Country X is a small country, with demand and supply functions for the food grains:QD = 150 - 0.6PQS = -40 + 0.5P where QD and QS are in millions of tons and P is the price per ton. The world price of grain is $200 per ton. a. In a situation of free trade, how much food grains would be produced, consumed, and traded in Country X?b. As a response to alleged unfair foreign practices, Country X farmers successfully lobby for a $20 export subsidy per ton of the grains exported. Assuming that imports of food grains are banned, show graphically and explain the impact of the export subsidy on domestic prices, consumption, production, and exports of grain by this country. Also indicate, using your graph, the effects on well-being of domestic producers and consumers and the cost of the
subsidy to the government, as well as the net change in well-being in Country X. For each of these changes, calculate the money amount of each of the changes in well-being and government cost.
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE:
a. Using the equations and the world price of $200, the quantity supplied of food grains by producers in Country X is 60 million tons and the quantity demanded of grains is 30 million tons. Therefore 30 million tons of food grains are exported by this country.
b. As Country X is a small country in the world market, there will be no effect on the world price when the export subsidy provided to the food grain producers in this country is implemented. For the food grain producers in Country X, the revenue per ton exported rises to $220, and the exporting firms must receive this amount as the selling price from domestic buyers as well. Domestic production rises from 60 to 70 million tons, domestic consumption falls from 30 to 18 million tons, and the country's exports increase from 30 million tons to (70 - 18) = 52 million tons. Domestic producers gain surplus equal to the area (e + f + g) or $1.3 billion, domestic consumers lose surplus equal to the area (e + f) or $480 million, and the cost to the government of paying the export subsidy is area (f + g + h) or $1.04 billion. The net loss in national well-being resulting from the export subsidy equals the sum of the areas f and h or $220 million.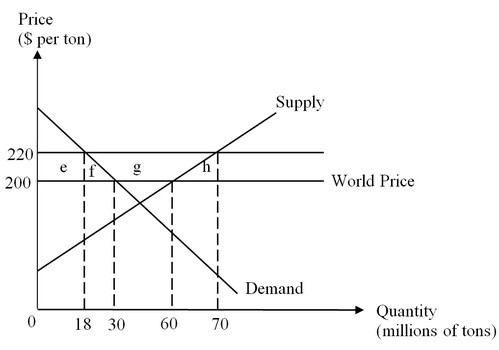
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 8-27. What is the level of disposable personal income for this economy?
A) $1,080 billion B) $1,010 billion C) $980 billion D) $860 billion
Suppose Winston's annual salary as an accountant is $60,000, and his financial assets generate $4,000 per year in interest. One day, after deciding to be his own boss, he quits his job and uses his financial assets to establish a consulting business, which he runs out of his home. To run the business, he outlays $8,000 in cash to cover all the costs involved with running the business, and earns revenues of $150,000. What are Winston's explicit costs?
A. $64,000 B. $72,000 C. $8,000 D. $12,000
A general definition of the "transmission mechanism" is: the routes or channels that ripple effects created in the
A) market for goods and the services travel to affect the money market. B) money market travel to affect the market for goods and services. C) labor market travel to affect the market for goods and services. D) market for goods and services travel to affect the labor market. E) none of the above
The better the information provided to financial markets the:
A. greater will be the flow of funds in these markets. B. greater the amount of funds transferred between savers and borrowers, though risk increases. C. higher the return required by lenders. D. less the amount of funds transferred between savers and borrowers.