Refer to Figure 15-6. The profit-maximizing output and price for the monopolist are
A) output = 62; price = $24. B) output = 104; price = $20.80.
C) output = 83; price = $22. D) output = 62; price = $18.
A
You might also like to view...
Analysts have attempted to model the impact of monetary policy on net worth by emphasizing
A) the impact of lower interest rates on business spending on fixed investment. B) the impact of lower interest rates on household spending on housing and durable goods. C) the liquidity of balance sheet positions as a determinant of business and household spending. D) the greater variability of business spending compared to household spending.
Refer to the table below. What is the probability of selling exactly 24 cakes?
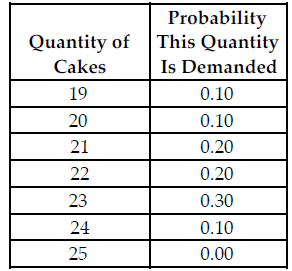
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
A) 0.20
B) 0.90
C) 0.00
D) 0.10
If perfectly competitive industry B is currently realizing economic profits, we would expect that:
a. industry output will fall, good B will fall in price, and economic profits will tend to disappear. b. industry output will fall, good B will rise in price, and economic profits will tend to disappear. c. industry output will rise, good B will fall in price, and economic profits will tend to disappear. d. industry output will rise, good B will fall in price, and economic profits will tend to increase.
The marginal rate of substitution measures
A) the impact of product substitution. B) the changes in marginal utility along the indifference curve. C) the consumer's willingness to substitute one product for another so that total utility will remain unchanged. D) the consumer's willingness to substitute one product for another so that marginal utility will remain unchanged.