Total factor productivity shocks are not a good explanation of economic fluctuations in the New Keynesian model for all the following reasons except
A) they do not generate output fluctuations.
B) employment drops when TFP increases.
C) the real wage drops when TFP increases.
D) they do not generate price fluctuations.
C
You might also like to view...
If, for a given percentage increase in price, quantity demanded falls by a proportionately smaller percentage, then demand is
A) relatively elastic. B) relatively inelastic. C) perfectly elastic. D) unit elastic.
At the uniform abatement standard described above, find total abatement costs for both firms.
Among the identified point sources contributing to the pollution of Puget Sound are Dow Chemical (D) and Chevron (C). Each firm's cost functions are shown below. MACD = 2.5AD MACC = 3.75AC TACD = 1.25AD2 TACC = 1.875AC2 To meet the effluent limits under the Clean Water Act, each firm has an NPDES permit to release some fixed amount of effluents, so each must abate 30 units.
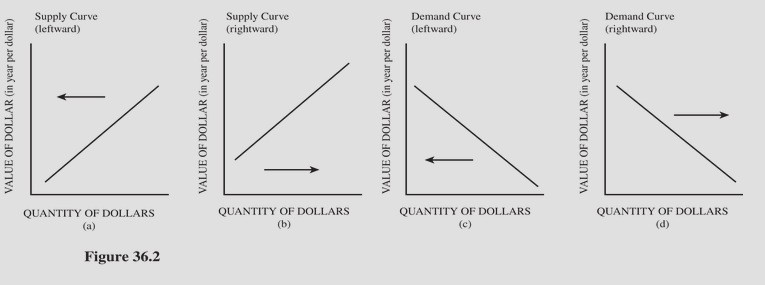 Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation, ceteris paribus: The Japanese remove some tariffs on American goods.
Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation, ceteris paribus: The Japanese remove some tariffs on American goods.
A. a. B. b. C. c. D. d.
As existing firms exit an increasing-cost industry
A. the position of the LRAC curve doesn't change, but firms move up their LRAC curve. B. the LRAC curve shifts down. C. the position of the LRAC curve doesn't change, but firms move down their LRAC curve. D. the LRAC curve shifts up.