What are the predictions for the long run equilibrium of the Monetary Approach?
What will be an ideal response?
Money supplies: Given the equations,
= PUS/PE
PUS = MUSS/L(R$, YUS)
PE = MES/L( , YE)
one can show that an increase in the U.S. money supply MUSS causes a proportional increase in the U.S. price level PUS, which in turn causes a proportional increase in . Thus, an increase in U.S. money supply causes a proportional long-run depreciation of the dollar against the euro and vice versa.
Interest rates: A rise in the interest rate R$ lowers U.S. money demand L(R$, YUS) thereby causing a rise in the U.S. price level and a proportional depreciation of the dollar against the euro.
Output levels: A rise in U.S. output YUS raises real U.S. money demand leading to a fall in the long-run U.S. price level and an appreciation of the dollar against the euro.
You might also like to view...
The short-run Phillips curve shows ________ between the unemployment rate and the inflation rate, and the long-run Phillips curve shows ________ between the unemployment rate and the inflation rate
A) a positive relationship; a negative relationship B) a negative relationship; a positive relationship C) no relationship; a negative relationship D) a negative relationship; no relationship E) no relationship; no relationship
A durable good is product that
A) holds up well under abuse. B) has had the same design over a long period of time. C) is purchased only once. D) is usable over a long period of time.
Any asset that sellers will accept as payment is a(n)
A) medium of exchange. B) unit of accounting. C) store of value. D) standard of deferred payment.
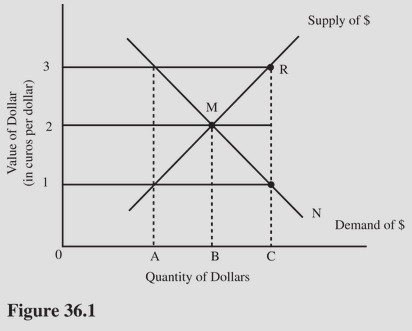 At an exchange rate of $1 = €1 in Figure 36.1, there is
At an exchange rate of $1 = €1 in Figure 36.1, there is
A. Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market. B. A shortage of euros. C. a shortage of dollars. D. A surplus of dollars.