Solve the problem.Assume that the price per unit d of a certain item to the consumer is given by the equation 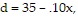 where x is the number of units in demand. The price per unit from the supplier is given by the equation
where x is the number of units in demand. The price per unit from the supplier is given by the equation 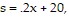 where x is the number of units supplied. Find the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity.
where x is the number of units supplied. Find the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity.
A. equilibrium price: $35 per unit; equilibrium quantity: 50 units
B. equilibrium price: $50 per unit; equilibrium quantity: 30 units
C. equilibrium price: $20 per unit; equilibrium quantity: 50 units
D. equilibrium price: $30 per unit; equilibrium quantity: 50 units
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Provide an appropriate response. Solve for x: 2x+1 = 23
A. x = -3 B. x = -2 C. x = 0 D. x = 2
An important calculation in calculus is the evaluation of the expression 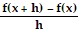 , where h ? 0. Find
, where h ? 0. Find 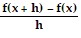 .f(x) = -14 - 5x
.f(x) = -14 - 5x
A. 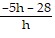
B. 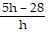
C. -5
D. 5
Solve the formula for the specified variable.-6k + ar = r - 9y for r
A. r = 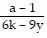 or r =
or r = 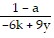
B. r = 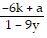 or r =
or r = 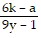
C. r = 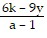 or r =
or r = 
D. r = 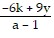 or r =
or r = 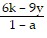
Use Bayes' rule to find the indicated probability.Two shipments of components were received by a factory and stored in two separate bins. Shipment I has 2% of its contents defective, while shipment II has 5% of its contents defective. If it is equally likely an employee will go to either bin and select a component randomly, what is the probability that a defective component came from shipment II?
A. 0.714 B. 0.222 C. 0.5 D. 0.2