A ball is projected upward at time t = 0.0 s, from a point on a roof 90 m above the ground. The ball rises, then falls and strikes the ground. The initial velocity of the ball is 36.2 m/s if air resistance is negligible
The time when the ball strikes the ground is closest to A) 9.4 s
B) 9.0 s
C) 8.7 s
D) 9.7 s
E) 10 s
A
You might also like to view...
Estimate the torque needed to rotate the inner cylinder at 1000 rpm if SAE-30 oil at 40°C fills the gap. Assume a linear velocity distribution in the gap. Neglect end effects.
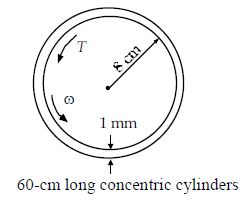
(A) 16.0 N·m
(B) 16.9 N·m
(C) 18.8 N·m
(D) 20.2 N·m
The boy plays "solitary seesaw" as shown. We can understand this by imagining that he has an invisible partner who is actually at the
1) fulcrum. 2) right end of the board. 3) rotational inertia of the seesaw as a whole. 4) seesaw's center of gravity. Since the seesaw is not rotating, we can say that 5) the net torque on the seesaw is zero. 6) potential energy and kinetic energy are equal to each other. 7) the boy's and the seesaw's centers of gravity must be equal distances from the fulcrum. 8) the boy and the seesaw must have the same weight.
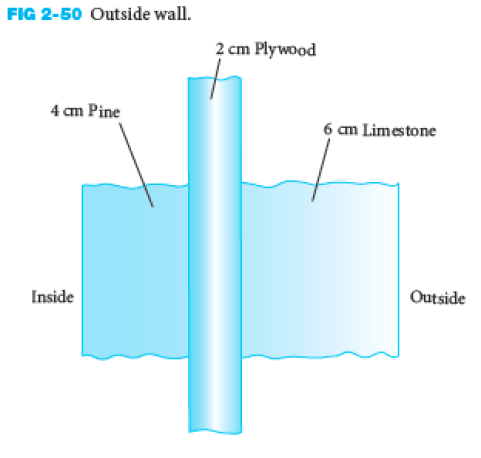
For the outside wall shown in Figure 2-50, determine the R-Value, the heat transfer through the wall per unit area and the temperature distribution through the wall if the outside surface temperature is 36ºC and the inside surface temperature is 15ºC.
An astronaut is piloting a spacecraft, which is in a circular orbit around Earth. A space station is ahead, on the same circular orbit. If he fires his rockets briefly to increase the forward speed of the rocket, what will happen?
What will be an ideal response?