Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.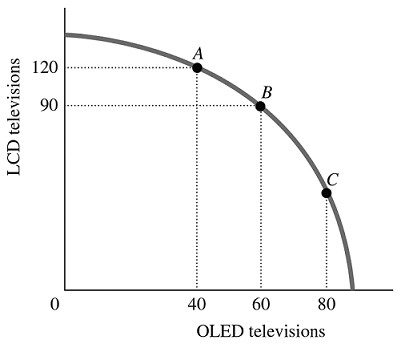 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point B. The opportunity cost of moving from Point B to Point A is the
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point B. The opportunity cost of moving from Point B to Point A is the
A. 120 LCD TVs that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED TVs.
B. 30 LCD TVs that must be forgone to produce 40 additional OLED TVs.
C. 20 OLED TVs that must be forgone to produce 30 additional LCD TVs.
D. 40 OLED TVs that must be forgone to produce 120 additional LCD TVs.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Negative Externality. Suppose there are no transactions costs. Also suppose the externality is internalized when the damaged parties offer producers a bribe of $5 per unit to reduce their production. Coase's analysis indicates that social gain in this situation will equal
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the effects of a negative externality created by an industry's production. The equilibrium quantity in the absence of any attempt to internalize the externality is QE, and the optimal quantity according to a Pigovian analysis is QO.
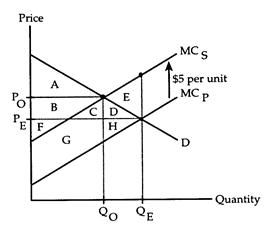
a. area A + B + F.
b. area A + B + F - E.
c. area A + B + C + D + F + G + H.
d. area A + B + C + F + G.
If Jet Cruises chooses to No Ad and Easy Sail then chooses to No Ad, Jet Cruises earns ________ million in net profit and Easy Sail earns ________ million.
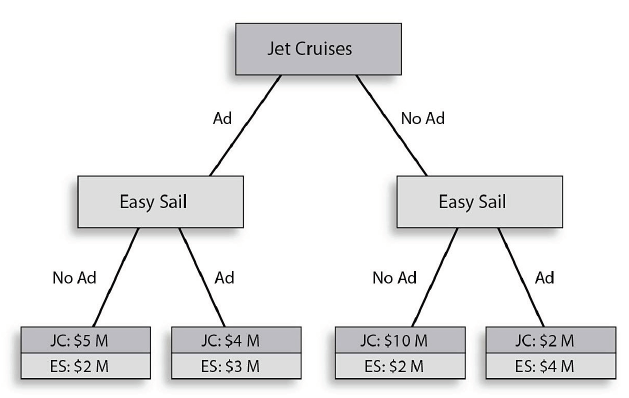
Jet Cruises wants to prevent Easy Sail from entering the sailboat market. The above game tree illustrates the different strategies and corresponding payoffs for the two firms. Both Jet Cruises and Easy Sail have the same strategies of advertising (Ad) or not advertising (No Ad). The payoffs represent net profit in millions.
A) $5; $2 B) $2; $4 C) $4; $3 D) $10; $2
Graphically inflation shocks shift the ________ and shocks to potential shift the ________.
A. long-run aggregate supply line; short-run aggregate supply line B. aggregate demand curve; long-run aggregate supply line C. aggregate demand curve; short-run aggregate supply line D. short-run aggregate supply line; long-run aggregate supply line
When there is only one buyer in a market, there is a
A. buyer's monopoly. B. buyer's cooperative. C. monopsony. D. monopoly.