Explain the relationship between the heat released by the chemical reaction and the change in temperature
The heat released is directly proportional to the change in temperature.
You might also like to view...
Which of these is NOT a consequence of resonance?
A) the Moon's periods of rotation and revolution are equal B) the orbital periods of Neptune and Pluto C) the Kirkwood Gaps in the asteroid belt D) Venus' cloud and surface rotation rates E) Mercury's rotation and revolution around the Sun
If a force on an object is aimed perpendicular to the direction of the object's velocity, the force does
a. no work. b. positive work. c. negative work. d. any of the above.
The magnitude of the Poynting vector of a planar electromagnetic wave has an average value of 0.724 W/m2
What is the maximum value of the magnetic field in the wave? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, ?0 = 4? × 10-7 T ? m/A, ?0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ? m2) A) 77.9 nT B) 55.1 nT C) 38.9 nT D) 108 nT E) 156 nT
Liquid oxygen at -183°C is stored in a thin walled spherical container with an outside diameter of 2 m. This container is surrounded by another sphere of 2.5 m inside diameter to reduce heat loss. The inner spherical surface has an emissivity of 0.05 and the outer sphere is black. Under normal operation the space between the spheres is evacuated but an accident resulted in a leak in the outer sphere and the space is filled with air at 100 kPa. If the outer sphere is at 25°C, compare the heat losses before and after the accident.
GIVEN
? A sphere filled with liquid oxygen surrounded by a larger sphere
? Sphere diameters ? Di = 2 m
? Do = 2.5 m
? Emissivity of inner sphere (?) = 0.05
? Outer sphere temperature (To) = 25°C = 298 K
? Liquid oxygen temperature (Ti) = –183° = 90 K
? Outer sphere is black
FIND
The rate of heat loss with
(a) A vacuum between the spheres
(b) Air at 100 kPa between the spheres
ASSUMPTIONS
? Steady state
? The internal convective resistance and the resistance of the inner sphere wall are negligible
SKETCH
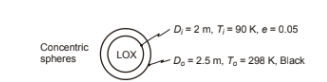
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
The thermal expansion coefficient (B) ? 1/T = 1/(194 K) = 0.0052 1/K
Extrapolating from Appendix 2, Table 27, for dry air at the mean temperature of –79°C from values at 0°C and 20°C
