Consider the boiling points of the following compounds and their solubilities in room-temperature water. Why does the solubilities in water go down as the boiling points of these alcohols go up.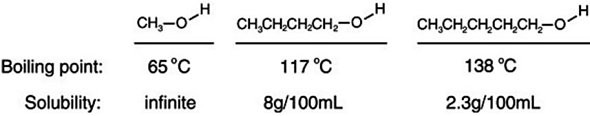
A. Larger molecules are more attracted to one another by induced dipole-induced dipole as well as by dipole-dipole and dipole-induced dipole attractions.
B. As the boiling increases, it is more difficult to keep the alcohol from evaporating out of solution.
C. Larger molecules are less attracted to one another by induced dipole-induced dipole as well as by dipole-dipole and dipole-induced dipole attractions.
D. As the boiling point increases, the size of the alcohol molecules decreases.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The salinity of seawater remains constant because
A. salinity measurement technology is unreliable. B. salts are removed from seawater about as fast as they are deposited. C. salts are included in the molecular formula of seawater. D. salts no longer form in the ocean.
Subsidence inversions are best developed in high pressure areas because the ____ air associated with them causes the air to ____
A) rising; cool B) sinking; cool C) rising; warm D) sinking; warm
Most organic compounds are made up of ________
A) carbon, nitrogen, and ozone atoms B) carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms C) nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide atoms D) carbon, nitrogen, and water atoms E) carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen atoms
The motion of a rock rolling downhill is known as ________ energy.
A. Electrical B. Potential C. Kinetic D. Mechanical E. Latent