Compute the average heat transfer coefficient hc for 10°C water flowing at 4 m/s in a long, 2.5-cm-ID pipe (surface temperature 40°C) by three different equations and compare your results. Also determine the pressure drop per meter length of pipe.
GIVEN
• Water flowing through a pipe
• Water temperature (Tb) = 10°C
• Water velocity (V) = 4 m/s
• Inside diameter of pipe (D) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Pipe surface temperature (Ts) = 40°C
FIND
(a) The average heat transfer coefficient ( h c) by 3 different equations.
(b) The pressure drop per meter length (?p/L)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Uniform and constant wall surface temperature
• Pipe wall is smooth
• Fully developed flow (L/D > 60)
SKETCH
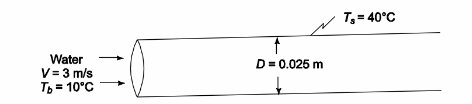
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for water at 10°C
for water at 10°C
Density (?) = 999.7 kg/m3
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.577 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 1.300 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 9.5
Absolute viscosity (?b) = 1296 × 10–6 (Ns)/m2
At the surface temperature of 40°C ?s = 658 × 10–6 (Ns)/m2
The Reynolds number for this problem is
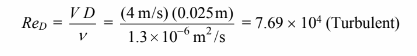
(a)
1. Using the Dittus-Boelter correlation
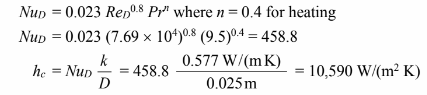
2. Using the Sieder-Tale correlation of

3. Using the Petukhov-Popov correlation of
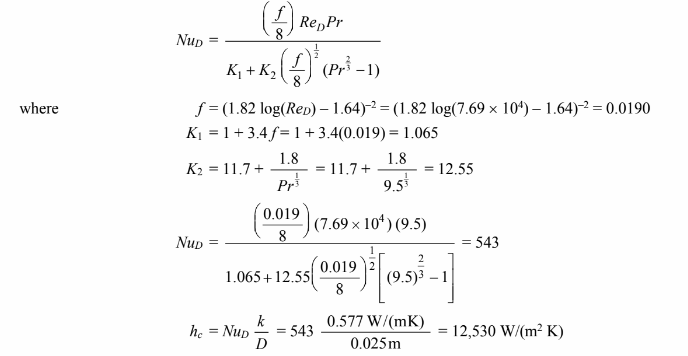
(b) The friction factor correlation of Equation (7.52) is good only for 1 × 105 < ReD. Therefore, the
friction factor will be estimated from the bottom curve of Figure 7.7: For Re = 7.69 × 104, f ? 0.0188 (Note that this is in good agreement with the friction factor, f in the Petukhov-Popov correlation). The pressure drop per unit length can be calculated
You might also like to view...
When a 12 volt car battery is short circuited with a wire, the current drawn from the battery is 100 amperes. The resistance of the wire is
a. zero b. 0.12 ohms c. 100/12 = 8.33 ohms d. 1200 ohms e. none of the above
Two converging lenses, the first with focal length 25 cm and the second with focal length 20 cm, are separated by 30 cm. A 4.0 cm tall object is placed 50 cm in front of the first lens. Which of the following characteristics does the final image have?
A. real and upright B. real and inverted C. virtual and upright D. virtual and inverted E. none of these choices are correct
Venus is brightest as seen from Earth:
A) at greatest eastern elongation, appearing half lit in the evening sky. B) at greatest western elongation, appearing half lit in the morning sky. C) 36 days before or after inferior conjunction, appearing as a large crescent. D) at inferior conjunction, when closest to Earth and largest in apparent size. E) at superior conjunction, and fully lit.
The order of evolutionary stages of a star like the Sun would be Main Sequence, giant, planetary nebula, and finally a ________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word