Public choice theory assumes voters, politicians, and other individuals in the public sector are largely motivated by
a. a desire to promote the general welfare.
b. a desire to meet the conditions of economic efficiency for the economy as a whole.
c. altruism or the good of the public as a whole.
d. personal self-interest.
D
You might also like to view...
Using Scenario 1 what would happen to your budget constraint if suddenly you discovered an extra 10 hours in your schedule that you could use to study
What would happen to the slope of the budget constraint? What would happen to the positioning of the budget constraint?
The distinction between real and nominal shocks is that
A) real shocks directly affect only the IS curve, but not the FE line or LM curve. B) real shocks directly affect only the FE line, but not the LM curve. C) real shocks directly affect only the IS curve or the FE line, but not the LM curve. D) real shocks have a large direct effect on the IS curve and the FE line, but only a small direct effect on the LM curve.
Refer to the accompanying figure. When P = 4, the price elasticity of demand for the demand curve D1 is ________ and D2 is ________.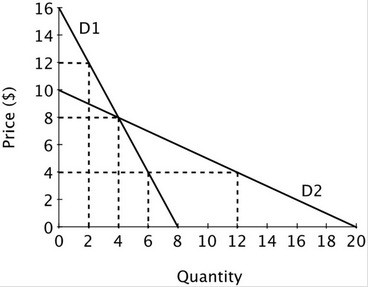
A. 1/3; 3 B. 3; 3 C. 1/3; 2/3 D. 2/3; 1/3
At the end of the year, Ford realizes it has overproduced Fiestas, because 2,500 of them are left unsold. How is this accounted for in that year's GDP? The cars are:
A. considered durable goods, and their value will increase consumption. B. considered inventory and their value will increase investment. C. not counted until they are sold in next year's GDP. D. considered a bad thing and reduce the value of investment.