The theory of perfect competition is built on several assumptions, including that
A) the individual firm can affect the price of the product it sells.
B) any firm can easily enter or leave the industry.
C) the individual firm can influence demand by advertising.
D) there are few producers of an identical product.
E) each firm must earn economic profits to remain in the industry.
Ans: B) any firm can easily enter or leave the industry.
You might also like to view...
Fiat money is:
a. includes currency and gold in bank vaults. b. does not include coins. c. is backed by any sort of commodity. d. has no value outside of its use as money.
Substitutes are pairs of goods that have a positive cross-price elasticity of demand
a. True b. False
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD3 to AD2 the result in the long run would be: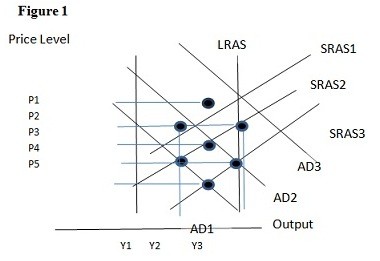
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y1. C. P3 and Y1. D. P3 and Y2.
Why does the trade-off between consumption goods and capital goods represent a trade-off between the present and the future?
What will be an ideal response?