Compare and contrast the effects of a tariff on prices and national well-being imposed in a small country with the effects of a tariff imposed in a large country. Illustrate your answer with the help of suitable diagrams.
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE: The figure below depicts the impact of a tariff imposed by a small country.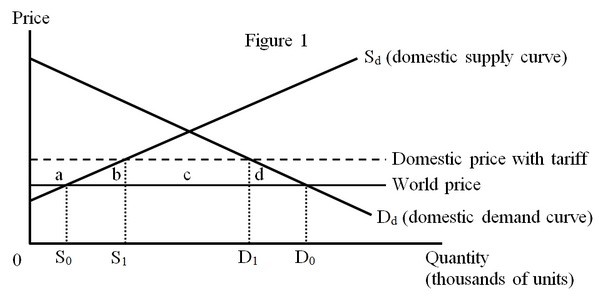
The figure below depicts the impact of a tariff imposed by a large country.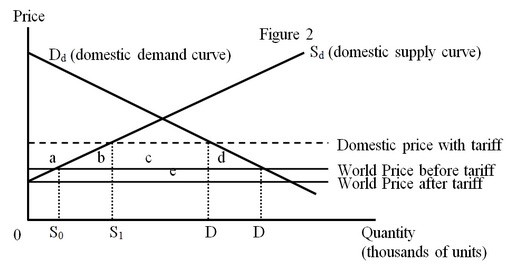
A tariff imposed by a small country will not have an impact on the world price of the good. So, the domestic price will rise by the amount of the tariff. A small country suffers welfare losses after the imposition of the tariff. Figure 1 illustrates the welfare implications of the tariff in a small country. The economic inefficiencies resulting from the tariff are measured by the sum of the production effect (area b) and the consumption effect (area d). As a result of the tariff, consumers lose the area (a + b + c + d), producers gain the area (a), and the government collects the area (c) in tariff revenues resulting in a net loss given by the sum of the area of the triangles b and d.
A tariff imposed by a large country will have an effect on the world price of the imported good. The large country collectively has monopsony power for the imported good. The importing country can exploit this monopsony power by reducing its demand for the imported good, so that the price it pays to the foreign exporters decreases. As shown in Figure 2, the world price will decrease once the tariff is imposed. The resulting effects on consumers and producers (areas a, b, c, and d) will be similar to the effects for the case of a small country. The difference (compared to the case of a small country) is the government tariff revenue. Area (e) measures the portion of the tariff that is effectively paid by the foreign exporters. The foreign exporters are compelled to sell their goods at a lower price after the tariff is imposed. Whether a large country eventually gains or losses from the tariff depends on whether the gain associated with the shift of the burden of the tariff to the foreigners, as shown by area (e), is larger or smaller than the domestic inefficiencies represented by the area (b + d).
You might also like to view...
Women bear a disproportionate burden in the agrarian system of Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia and Latin America. In addition their productivity is low. Explain these statements with specific examples from individual developing economies
What measures/policies have been implemented to deal with these two issues? Once again discuss with specific examples from individual developing economies.
Which of the following is the most likely cause of a recession according to the real business cycle model?
a. an unanticipated change in the money supply. b. an increase in taxation, government spending, and regulation. c. a fall in expected profits. d. an anticipated change in the money supply. e. none of the above.
To find the market demand curve for a product, we sum the individual demand curves a. vertically
b. diagonally. c. horizontally. d. perpendicularly.
By lowering the legal reserve requirement, the Federal Reserve System forces banks to hold repaid loans as required reserves instead of lending the funds again
Indicate whether the statement is true or false