If deflation occurs and your income is fixed, your real income:
What will be an ideal response?
will go up.
You might also like to view...
If a perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue was less than its marginal cost, a. it would raise its price in order to increase its profits
b. it would contract its output but not raise its price in order to increase its profits. c. it is currently earning economic losses. d. both (a) and (c) are true.
Using the indifference curve model, a demand for X curve is derived by allowing:
A. the price of Y to change and holding the price of X and income constant. B. income to change and holding the price of X and the price of Y constant. C. the price of X and the price of Y to change and holding income constant. D. the price of X to change and holding the price of Y and income constant.
Refer to the below graph. Consider a situation where price increases from P3 to P4. In this price range, demand is relatively:
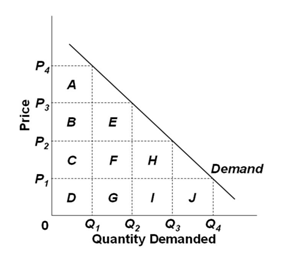
A. Inelastic because the loss in total revenue (areas E + F + G) is greater than the gain in total revenue (area A)
B. Elastic because the loss in total revenue (areas E + F + G) is greater than the gain in total revenue (area A)
C. Elastic because the loss in total revenue (area A) is greater than the gain in total revenue (areas E + F + G)
D. Inelastic because the loss in total revenue (area A) is greater than the gain in total revenue (areas E + F + G)
An inflation rate above the target rate will result in:
A. a movement up along the monetary policy reaction curve and a rightward shift of the dynamic aggregate demand curve. B. a movement up along the monetary policy reaction curve and a leftward shift of the dynamic aggregate demand curve. C. a movement up along the monetary policy reaction curve and a movement up the dynamic aggregate demand curve. D. a movement down along the monetary policy reaction curve and a movement down the dynamic aggregate demand curve.