Repeat exercise 15.24 for the following different set of functional dependencies G = { {A, B} -> {C}, {B, D} -> {E, F}, {A, D} -> {G, H}, {A} -> {I}, {H} -> {J} }.
What will be an ideal response?
```
To help in solving this problem systematically, we can first find the closures of all
single attributes to see if any is a key on its own as follows:
{A}+ -> {A, I}, {B}+ -> {B}, {C}+ -> {C}, {D}+ -> {D}, {E}+ -> {E}, {F}+ -> {F},
{G}+ -> {G}, {H}+ -> {H, J}, {I}+ -> {I}, {J}+ -> {J}
Since none of the single attributes is a key, we next calculate the closures of pairs of
attributes that are possible keys:
{A, B}+ -> {A, B, C, I}, {B, D}+ -> {B, D, E, F}, {A, D}+ -> {A, D, G, H, I, J}
None of these pairs are keys either since none of the closures includes all attributes. But
the union of the three closures includes all the attributes:
{A, B, D}+ -> {A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I}
Hence, {A, B, D} is a key. (Note: Algorithm 15.4a (see chapter 15 in the textbook) can
be used to determine a key).
Based on the above analysis, we decompose as follows, in a similar manner to problem
14.26, starting with the following relation R:
R = {A, B, D, C, E, F, G, H, I}
The first-level partial dependencies on the key (which violate 2NF) are:
{A, B} -> {C, I}, {B, D} -> {E, F}, {A, D}+ -> {G, H, I, J}
Hence, R is decomposed into R1, R2, R3, R4 (keys are underlined):
R1 = {A, B, C, I}, R2 = {B, D, E, F}, R3 = {A, D, G, H, I, J}, R4 = {A, B, D}
Additional partial dependencies exist in R1 and R3 because {A} -> {I}. Hence, we remove
{I} into R5, so the following relations are the result of 2NF decomposition:
R1 = {A, B, C}, R2 = {B, D, E, F}, R3 = {A, D, G, H, J}, R4 = {A, B, D}, R5 = {A, I}
Next, we check for transitive dependencies in each of the relations (which violate 3NF).
Only R3 has a transitive dependency {A, D} -> {H} -> {J}, so it is decomposed into R31
and R32 as follows:
R31 = {H, J}, R32 = {A, D, G, H}
The final set of 3NF relations is {R1, R2, R31, R32, R4, R5}
```
You might also like to view...
Explain how Router1, in the previous example, knows that datagram destined to network 10.0.3.10 should be forwarded 10.0.2.2?
What will be an ideal response?
________ prevents someone from accessing sensitive information
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
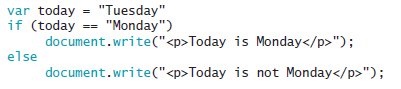 The output of the accompanying code is ____.
The output of the accompanying code is ____.
A. "Today is Tuesday" will be printed B. Nothing will be printed C. "Today is Monday" will be printed D. "Today is not Monday" will be printed
Widths in media queries are based on the width of the visual viewport.?
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)