Suppose the economy has been experiencing zero inflation and 5 percent unemployment for several years. The government decides to lower the unemployment by generating some inflation. Using a graph, show what the short-run effects would be and what would happen in the long run. What would the government have to do to keep the unemployment rate at 3 percent?
What will be an ideal response?
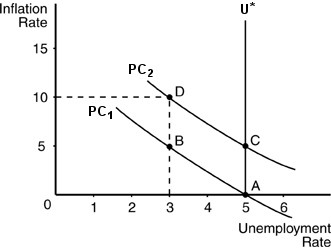
See above figure. The natural rate of unemployment is 5 percent. The government inflates by pursuing expansionary monetary policy and the economy moves to B, with an unemployment rate of 3 percent and inflation rate of 5 percent. In the long run, the Phillips curve shifts to the right and the unemployment rate goes back to 5 percent. For the government to maintain 3 percent unemployment, it would have to keep increasing the inflation rate (point D).
You might also like to view...
Which one of the following is NOT a key trade-off a society faces?
A) Who gets the goods and services B) Who produces the goods and services C) Which goods and services to produce D) How to produce
What is the average cost per unit for producing 3 units? a. 200. b. 260. c. 70
d. 110.
The relationship between changes in income and purchase of a good indicates
a. whether the good is a luxury or necessity. b. whether the good is normal or inferior. c. whether the good is a complement or substitute. d. Both a and b.
A firm enjoys a positive economic profit when:
a. the demand curve touches the average cost curve at the profit-maximizing level of output. b. the marginal revenue curve has a negative intercept on the ordinate axis. c. the average revenue curve lies below the average cost curve at the profit-maximizing level of output. d. the marginal cost is declining at the profit-maximizing level of output. e. the average revenue curve lies above the average cost curve at the profit-maximizing level of output.