Why does the price level in a perfectly competitive market move toward the zero-profit point?
a. Because firms enter and exit the market in response to gains and losses
b. Because short-run losses reverse the effects of long-run gains
c. Because profitable firms increase short-run productivity
d. Because firms operate below the average cost curve
a. Because firms enter and exit the market in response to gains and losses
You might also like to view...
In New York City, about 1 million apartments are subject to rent control by the local government. Rent control
A) puts a legal limit on the rent that landlords can charge for an apartment. B) is a government policy which limits apartment rental to those people whose incomes are less than $50,000 per year. C) is a price floor which sets a minimum rent for apartments. D) only applies to those apartments which are owned and rented out by the local government.
Items subtracted from tax liability are called _____
a. tax credits b. tax deductions c. tax exemptions d. tax exclusions
A restaurant chain announces declining revenues. What's the name of the type of risk that this news raises for holders of this chain's bonds? What does this news to do the interest rate on this chain's bonds?
Use the following graph to answer the next question.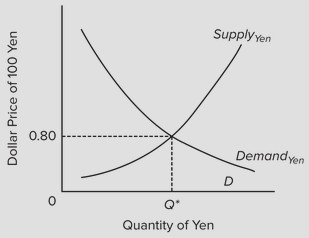 Assume that Japan and the United States are engaged in a system of flexible exchange rates. An increase in the demand for yen will result in a(n) ________.
Assume that Japan and the United States are engaged in a system of flexible exchange rates. An increase in the demand for yen will result in a(n) ________.
A. appreciation of the U.S. dollar B. decrease in the dollar price of yen C. depreciation of the U.S. dollar D. depreciation of the Japanese yen