A business manager has to decide whether to buy supplies from the marketplace or whether to build them inside the company. What do "information" and "contracting" have to do with this decision?
What will be an ideal response?
Contracting costs and the costs of acquiring specific knowledge or specific information play a large role in the decision of whether transactions occur in the marketplace or within the boundaries of the firm. Firms are more efficient than markets at organizing some transactions when the costs of information gathering and contracting in markets are high. However, when information is available at a lower cost and contracting or transactional costs are low in the marketplace, it is more efficient for transactions to occur in the marketplace. Individuals have a strong incentive to organize transactions efficiently to maximize gains from trade.
You might also like to view...
If aggregate demand decreases, the
A) short-run Phillips curve shifts rightward. B) economy moves to a higher inflation rate along its short-run Phillips curve. C) short-run Phillips curve does not shift nor is there a movement along it. D) short-run Phillips curve shifts leftward. E) economy moves to a lower inflation rate along its short-run Phillips curve.
In many corporations, there is "separation of ownership from control." What does this mean?
A) The board of directors controls corporate operations, although the managers of the corporation own the corporation. B) Top corporate managers only make decisions that have been approved unanimously by shareholders. C) The shareholders control the corporation, although the board of directors owns the corporation. D) The managers of the corporation run the corporation, although the shareholders own the corporation.
When per capita real GDP is increasing, real output is growing
a. more rapidly than prices. b. more rapidly than population. c. less rapidly than prices. d. less rapidly than population.
Refer to the graph shown. Given the production possibility curve, the opportunity cost of reading 2 more articles when you are already reading 11 articles is on average: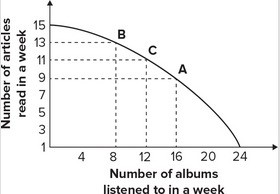
A. 2 albums per article. B. 3 albums per article. C. 1/2 album per article. D. 2/3 album per article.