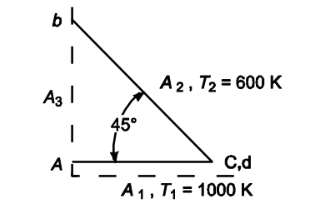
The wedge-shaped cavity shown in the accompanying sketch consists of two long strips joined along one edge. Surface 1 is 1-m-wide, has an emittance of 0.4, and has a temperature of 1000 K. The other wall has a temperature of 600 K. Assuming gray diffuse processes and uniform flux distribution, calculate the rate of energy loss from surface 1 and 2 per meter length.
GIVEN
• The wedge shaped cavity shown above
• Width of A1 (W1) = 1 m
• Emittance of A1 (?1) = 0.4
• Temperature of A1 (T1) = 1000 K
• Temperature of A2 (T2) = 600 K
• A2 is black
FIND
• The rate of energy loss from A1 and A2 per meter length (q1/L and q2/L)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Enclosure temperature (Te) = 0 K
• Gray diffuse processes
• Uniform flux distribution
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
Width of A3 (W3) = 1 m
Width of A2 (W2) = 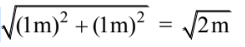
The crossed-string methods can be used to calculate F12.
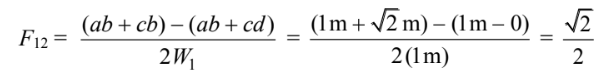

Since neither A1 nor A2 can see itself, F11 = F22 = 0
Since A2 is black: ?2 = 0 and ?2 = 1
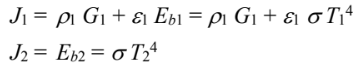
for A1
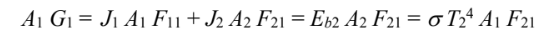
Solving for G1
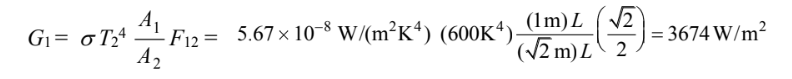
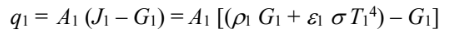

for A2

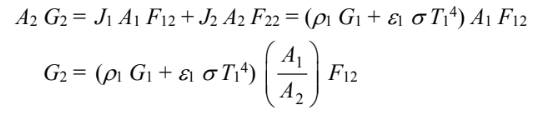
Since ?1 = 1 – ?1
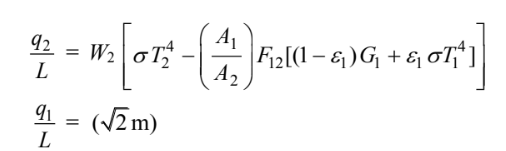

You might also like to view...
Which of the following stars is a luminous red supergiant and is classified M2 Ia?
A) Spica B) Betelgeuse C) Pollux D) Miaplacidus
A 1.86-kg block is held in place against the spring by a 81-N horizontal external force (see the figure). The external force is removed, and the block is projected with a velocity v1 = 1.2 m/s upon separation from the spring
The block descends a ramp and has a velocity at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction over this section is 0.28. The velocity of the block is v3 = 1.4 m/s at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. The height h of the ramp is closest to A) 11 B) 7.3 C) 15 D) 17 E) 18
What is the wavelength of a 1-hertz electromagnetic wave?
A) less than 1 m B) 1 m C) more than 1 m
The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5.3 years, while that of strontium-90 is 28 years. Suppose that samples of cobalt-60 and strontium-90 are such that they initially have the same activity (number of decays per second)
What is true about the initial numbers of cobalt-60 and strontium-90 nuclei in these samples? A) There are more strontium-90 than cobalt-60 nuclei. B) There are equal numbers of cobalt-60 and strontium-90 nuclei. C) It is not possible to compare numbers of nuclei without knowing the masses of the samples. D) There are more cobalt-60 than strontium-90 nuclei.