Suppose the government increases the annual cost of the liquor permit that a tavern needs to serve alcohol. What effect will this increased cost have on the tavern's production and pricing decisions?
a. None-the tavern will maintain its current prices.
b. The tavern will raise its prices to cover the higher cost.
c. The tavern will scale back its operations.
d. The tavern will cut its prices to increase its sales.
a. None-the tavern will maintain its current prices.
You might also like to view...
Robert Lucas Jr. adapted the fooling model to his own way of thinking by replacing that model's assumption of
A) continuous market-clearing. B) imperfect information. C) the natural rate hypothesis. D) the gradual correction of expectational errors.
Suppose a monopoly firm has an annual demand function of Qd = 20,000 - 250P, annual variable costs of VC = 16Q + 0.002Q2 and marginal cost of MC = 16 + 0.004Q, where Q is the annual quantity of output. In addition, the firm has an avoidable fixed cost of $25,000 per year. If this firm maximizes its profit, what is the value of its producer surplus?
A. $156,500 B. $181,500 C. $242,000 D. $217,000
Which of the following is true any place on the production possibilities curve?
a. Producing more of one item creates less of the other. b. Both items must be produced in equal volumes. c. Only one item may be produced at a time. d. No items can be produced if there is inefficiency.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 1.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.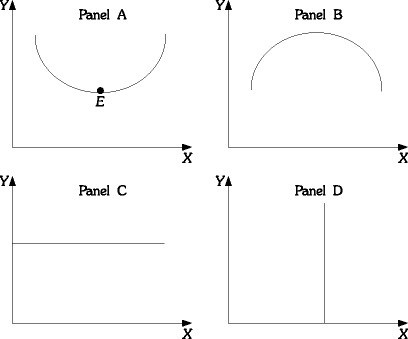 Figure 1.4Refer to Figure 1.4. At Point E in Panel A, the slope is
Figure 1.4Refer to Figure 1.4. At Point E in Panel A, the slope is
A. zero. B. infinite. C. negative. D. indeterminate from this information.