Discuss probable incidence of a local tax on business property
What will be an ideal response?
A local tax on business property could be shifted to the tenant if the landlord is someone other than the business owner. The business, whether tenant or property owner, could shift some of the property tax to customers in the form of higher prices. The degree to which the tax could be shifted would depend on the impact the tax had on the firm’s product prices. If demand for the firm’s product was very elastic, then the firm would be unable to raise prices by the full amount of the tax, and the firm would bear the burden of the tax in the form of reduced profits. If demand for the firm’s product was inelastic and the tax did not raise prices significantly, then the firm could pass on the cost of the property tax to its customers.
You might also like to view...
In the foreign exchange market, a broker reveals the names of the banks making bids or offers to the trading banks before the trade has been agreed upon
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Which of the following is most likely to be TRUE?
A) Income elasticity of demand for fur coats exceeds that of oatmeal. B) Income elasticity of demand for oatmeal exceeds that of fur coats. C) Income elasticity of demand for fur coats equals that of oatmeal. D) It is not possible to make any prediction about relative income elasticities.
Refer to the accompanying figure.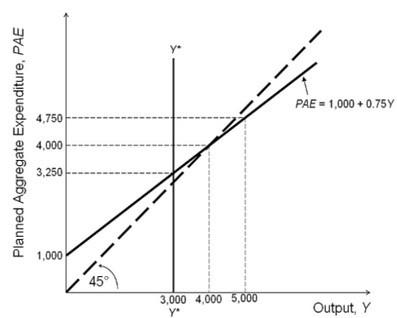 Based on the Keynesian cross diagram, short-run equilibrium output equals:
Based on the Keynesian cross diagram, short-run equilibrium output equals:
A. 4,000. B. 3,250. C. 3,000. D. 4,750.
When the economy is at its equilibrium GDP level, all of the following will occur, except:
A. Aggregate expenditures = GDP B. Inventories will be zero C. Saving equals planned investment D. There are no unplanned changes in inventories