Patterns of stars in constellations hardly change in appearance over times of even a few thousand years. Why?
A) Stars are fixed and never move.
B) Stars move, but they move very slowly—only a few kilometers in a thousand years.
C) Although most stars move through the sky, the brightest stars do not, and these are the ones that trace the patterns we see in the constellations.
D) The stars in our sky actually move rapidly relative to us—thousands of kilometers per hour—but are so far away that it takes a long time for this motion to make a noticeable change in the patterns in the sky.
E) Stars within a constellation move together as a group, which tends to hide their actual motion and prevent the pattern from changing.
D
You might also like to view...
Size of the Nucleus: If an atomic nucleus containing 64 nucleons has a radius R, what will be the expected radius of a nucleus containing 512 nucleons?
A. R B. 2R C. 4R D. 8R E. 16R
What is the equivalent capacitance of the combination shown?
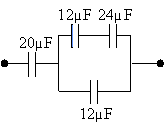
a.
29 µF
b.
10 µF
c.
40 µF
d.
25 µF
The ionosphere is an electrified ion-rich area
A) in the uppermost troposphere. B) where atoms lose their electrons and are negatively charged. C) where air density and solar radiation is low. D) within the uppermost mesosphere and thermosphere.
Two continuous waves having the same wavelength and amplitude pass through the same medium. They are aligned crest to crest and trough to trough so that they interfere. The resulting wave has
A) the same wavelength and the same amplitude. B) twice the wavelength and twice the amplitude. C) zero amplitude. D) twice the wavelength and the same amplitude (or height) as each of the individual waves. E) the same wavelength and twice the amplitude.