Describe the effects of the concentration and electrical gradients on the movement of Na+ and K+ ions through the membrane
What will be an ideal response?
The unequal diffusion and unequal pumping of cations (Na+ and K+) causes the ECF side of the plasma membrane to be positively charged while the ICF side is negatively charged. As the inside border of the membrane becomes more negative, it exerts a stronger attraction for the K+ ions, which prevents an excessive amount of K+ diffusion out of the cell. Although the negative inside border has a very strong attraction for the Na+ ions in the ECF, the membrane is not very "leaky" to these ions. However, if a channel opens and allows these ions to passively move through the membrane, Na+ ions will move into the cell down its concentration gradient and down the electrical gradient (i.e., from a positive region toward a negative region). Potassium ions can diffuse out of the cell along their concentration gradient, but it would be against an electrical gradient, unless the outside border becomes negatively charged.
You might also like to view...
The appendicular skeleton includes bones of the thorax, spinal column, hyoid bone, bones of the middle ear, and skull.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Identify the thin protective mucous membrane composed of stratified squamous epithelium with numerous goblet cells
a) A and B b) B and D c) C and A d) D and C e) B and E
The function of structure E is
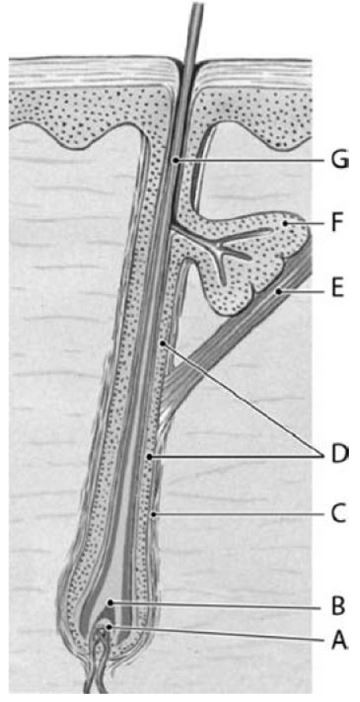
A) to attach the hair shaft firmly to the dermis so that it does not move.
B) the deposition of high concentrations of melanin to color the hair shaft.
C) the production of new cells that will make the hair shaft longer.
D) the production of hormones that can affect the growth cycles of the hair follicle.
E) to change the orientation of the hair shaft.
Which type of tissue acts a firm, protective packing around and between organs?
a. cartilage b. adipose c. epithelial d. nervous