Suppose all firms in a competitive market are currently in both short-run and long-run equilibrium. What impact will a lump sum tax have on each firm in the short run? in the long run?
What will be an ideal response?
In the short run, the lump sum tax represents a fixed cost. The firm's output decision is unchanged, but its profits decrease. In the long run, the tax raises the LRAC of each firm, but not MC. Minimum AC is higher, so price is higher. With a higher price, each firm produces a greater quantity, but the higher price means less quantity is demanded in total; thus, the number of firms will decrease.
You might also like to view...
The monetary policies carried out by the Fed
a. must be ratified by Congress. b. must be consistent with fiscal policies passed by Congress. c. are sometimes inconsistent with fiscal policy. d. must be approved by the president.
A move from S4 to S1 is a(n)
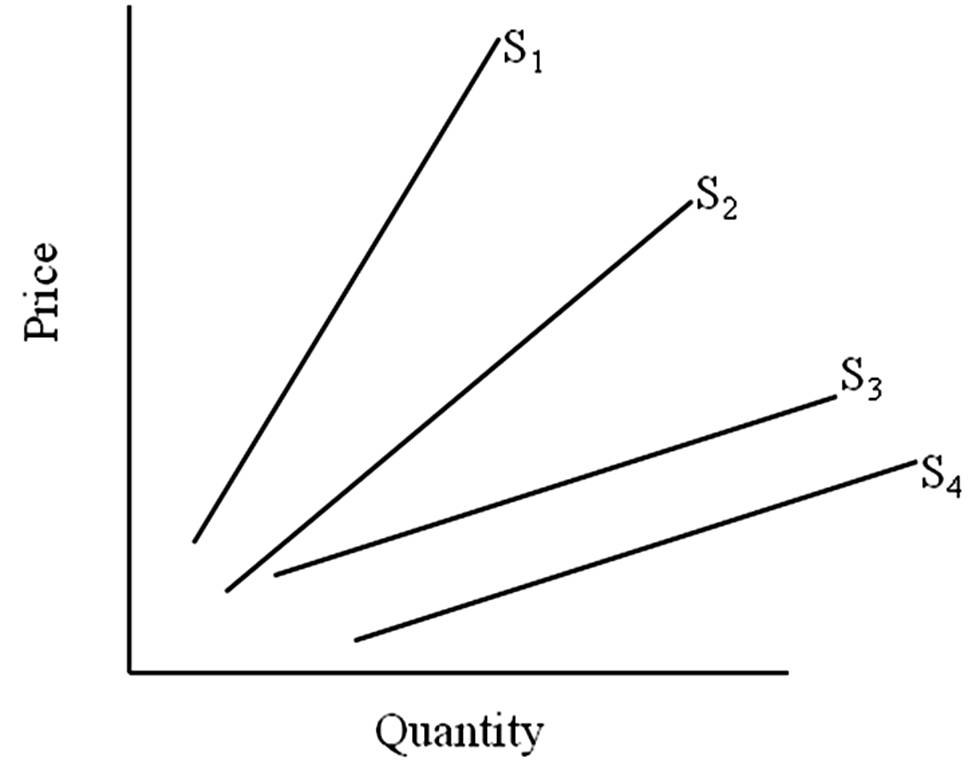
A. an increase in quantity supplied.
B. a decrease in quantity supplied.
C. an increase in supply.
D. a decrease in supply.
At the beginning of the fall semester, college towns experience large increases in their populations, causing a(n):
A. decrease in the quantity of apartments supplied. B. increase in the demand for apartments. C. increase in the supply of apartments. D. decrease in the quantity of apartments demanded.
For the monopolist, marginal revenue is
A) equal to price. B) less than average revenue since price must be lowered to sell additional units. C) greater than price. D) not a consideration in the firm's pricing.