For a competitive firm, the marginal cost curve
A. the short-run supply curve at all viable production levels
b. shifts to the upward when new firms enter the market.
c. shifts upward when wages decrease.
d. is the short-run demand curve.
Ans: A. the short-run supply curve at all viable production levels
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 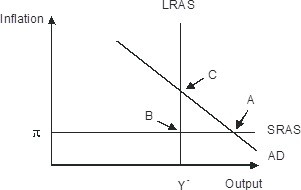
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
The maximum amount of production that can be produced while avoiding shortages of labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship that would bring rising inflation is called
A) real GDP. B) nominal GDP. C) actual GDP. D) potential GDP.
Marginal utility is the
A) usefulness of a product. B) utility that a person receives from the consumption of goods and services. C) change in utility that results from a one-unit change in the quantity of a good consumed. D) change in utility that results from a one-unit change in the price of a good consumed.
David Elkind, author and child expert, says that:
a. Children do not have enough to do b. Children have too much free time c. Children are overcommitted and growing up too fast and too soon d. Children spend too much time in unorganized activities