Elastic Collisions: In a perfectly elastic collision, a 400-g ball moving toward the east at 3.7 m/s suddenly collides head-on with a 200 g ball sitting at rest.(a) Determine the velocity of the first ball just after the collision.(b) Determine the velocity of the second ball just after the collision.(c) Is kinetic energy conserved in this collision? How do you know?
What will be an ideal response?
(a) 1.2 m/s toward the east (b) 4.9 m/s toward the east (c) Yes, it is an elastic collision.
You might also like to view...
The point P lies along the perpendicular bisector of the line connecting two long straight wires S and T that are perpendicular to the page. A set of directions A through H is shown next to the diagram. When the two equal currents in the wires are directed up out of the page, the direction of the magnetic field at P is closest to the direction of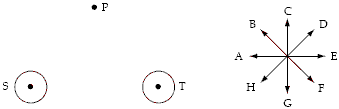
A. E. B. F. C. G. D. H. E. A
A __________ is a three-dimensional image made using a laser
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
The figure shows a distance vs. time graph of an object with three distinct regions, I, II, and III
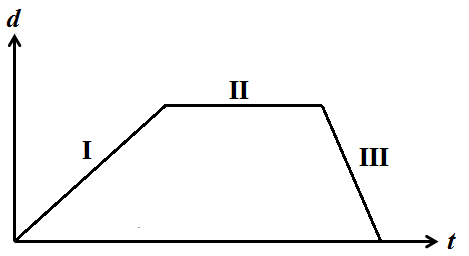 ?
?
The object’s velocity is positive in region II.
a.
True
b.
False
Einstein's theory of relativity is based in part on which one of the following postulates?
a. Speed of light in a vacuum is same for all observers regardless of source velocity. b. Energy is conserved only in elastic collisions. c. Space and time are absolutes. d. Mass and energy are equivalent.