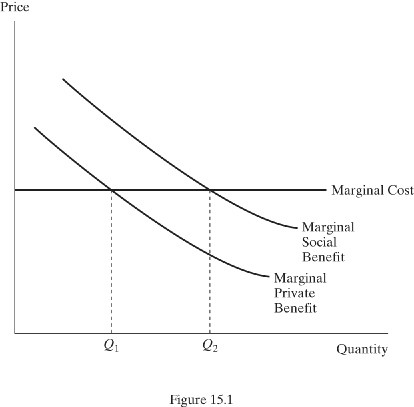
 In the market in Figure 15.1, the government, in theory, can get the socially optimum output by:
In the market in Figure 15.1, the government, in theory, can get the socially optimum output by:
A. subsidizing the consumption of the good by the right amount.
B. taxing the production of the good by the right amount.
C. restricting the production of the good to less than what the market produces.
D. All of these
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A contractionary monetary policy can reduce the inflation rate without causing a rise in unemployment if expectations are formed rationally and monetary policy is
A) combined with expansionary fiscal policy. B) carried out in total secrecy. C) publicly announced and credible. D) combined with contractionary fiscal policy.
Suppose that the price of telephones decreases. If more are purchased then:
a. the total utility of telephones will decrease. b. the total utility of telephones will be unchanged. c. the marginal utility of telephones will likely increase. d. the marginal utility of telephones will likely decrease. e. both a and d.
In a perfectly competitive market:
A. only price adjusts in both the short run and the long run. B. only quantity adjusts in both the short run and the long run. C. price does more of the adjusting in the short run and quantity does more of the adjusting in the long run. D. price does more of the adjusting in the long run and quantity does more of the adjusting in the short run.
An increase in public works spending is likely to
A. Have no effect on physical capital investment. B. Increase transportation costs and environmental impact. C. Decrease physical capital investment. D. Increase market efficiency.