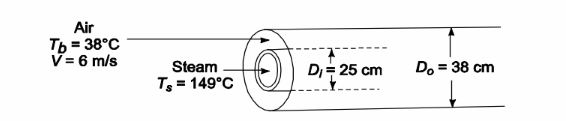
Atmospheric pressure air is heated in a long annulus (25-cm-ID, 38-cm-OD) by steam condensing at 149°C on the inner surface. If the velocity of the air is 6 m/s and its bulk temperature is 38°C, calculate the heat transfer coefficient.
GIVEN
Atmospheric flow through an annulus with steam condensing in inner tube
Inside diameter (Di) = 25 cm = 0.25 m
Outside diameter (Do) = 38 cm = 0.38 m
Steam temperature (Ts) = 149°C
Air velocity (V) = 6 m/s
Air bulk temperature (Tb) = 38°C
FIND
The heat transfer coefficient (hc)
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Steam temperature is constant and uniform
Heat transfer to the outer surface is negligible
Air temperature given is the average air temperature
Thermal resistance of inner tube wall and condensing steam is negligible (Inner tube wall surface
temperature = Ts)
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at 38°C
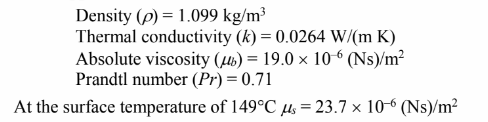
the hydraulic diameter of the annulus is given by
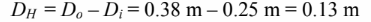
The Reynolds number based on this diameter is
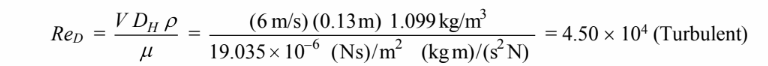
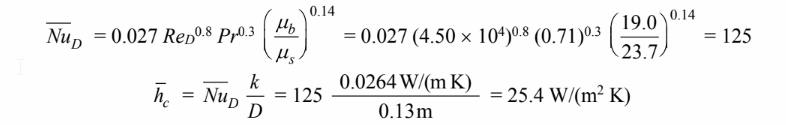
Applying the Sieder-Tale correlation
You might also like to view...
The mysterious component if the universe which appears to be pushing galaxies apart is referred to as
A) dark energy B) anti-gravity C) dark matter D) inflation
A student has made the statement that the electric flux through one half of a Gaussian surface is always equal and opposite to the flux through the other half of the Gaussian surface. This is
a. never true. b. never false. c. true whenever enclosed charge is symmetrically located at a center point, or on a center line or centrally placed plane. d. true whenever no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface. e. true only when no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface.
If TiNi is deformed 5 % at a temperature above the martensite start temperature, and then the strain is fully recovered upon reduction of the stress to 0, this material is
(a) Super or pseudoelastic. (b) Anelastic. (c) Elastic. (d) Plastic.
The supernova that created the Crab nebula and its pulsar was seen on Earth in the year
A) 1604 BC. B) 1054 BC. C) 1054 AD. D) 1592 AD. E) 1604 AD.